A compilation of the Top 50 matplotlib plots most useful in data analysis and visualization. This list lets you choose what visualization to show for what situation using python’s matplotlib and seaborn library.
Introduction
The charts are grouped based on the 7 different purposes of your visualization objective. For example, if you want to picturize the relationship between 2 variables, check out the plots under the ‘Correlation’ section. Or if you want to show how a value changed over time, look under the ‘Change’ section and so on.
An effective chart is one which:
- Conveys the right and necessary information without distorting facts.
- Simple in design, you don’t have to strain in order to get it.
- Aesthetics support the information rather than overshadow it.
- Not overloaded with information.
Matplotlib is popularly used for visualizing plots. Check out these free video tutorials to learn how to get started with Matplotlib and create your your first plot.
__Related Posts: __
Matplotlib Full Tutorial
Matplotlib Subplots
Contents
(right click and open in new page if the links don’t work)
Correlation
- Scatter plot
- Bubble plot with Encircling
- Scatter plot with line of best fit
- Jittering with stripplot
- Counts Plot
- Marginal Histogram
- Marginal Boxplot
- Correlogram
- Pairwise Plot
Deviation
Ranking
Distribution
- Histogram for Continuous Variable
- Histogram for Categorical Variable
- Density Plot
- Density Curves with Histogram
- Joy Plot
- Distributed Dot Plot
- Box Plot
- Dot + Box Plot
- Violin Plot
- Population Pyramid
- Categorical Plots
Composition
Change
- Time Series Plot
- Time Series with Peaks and Troughs Annotated
- Autocorrelation Plot
- Cross Correlation Plot
- Time Series Decomposition Plot
- Multiple Time Series
- Plotting with different scales using secondary Y axis
- Time Series with Error Bands
- Stacked Area Chart
- Area Chart Unstacked
- Calendar Heat Map
- Seasonal Plot
Groups
Setup
Run this once before the plot’s code. The individual charts, however, may redefine its own aesthetics.
If you want to have a video walkthrough of how to setup Matplotlib, check this free video lesson.
# !pip install brewer2mpl
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import warnings; warnings.filterwarnings(action='once')
large = 22; med = 16; small = 12
params = {'axes.titlesize': large,
'legend.fontsize': med,
'figure.figsize': (16, 10),
'axes.labelsize': med,
'axes.titlesize': med,
'xtick.labelsize': med,
'ytick.labelsize': med,
'figure.titlesize': large}
plt.rcParams.update(params)
plt.style.use('seaborn-whitegrid')
sns.set_style("white")
%matplotlib inline
# Version
print(mpl.__version__) #> 3.0.0
print(sns.__version__) #> 0.9.0
Correlation
The plots under correlation is used to visualize the relationship between 2 or more variables. That is, how does one variable change with respect to another.
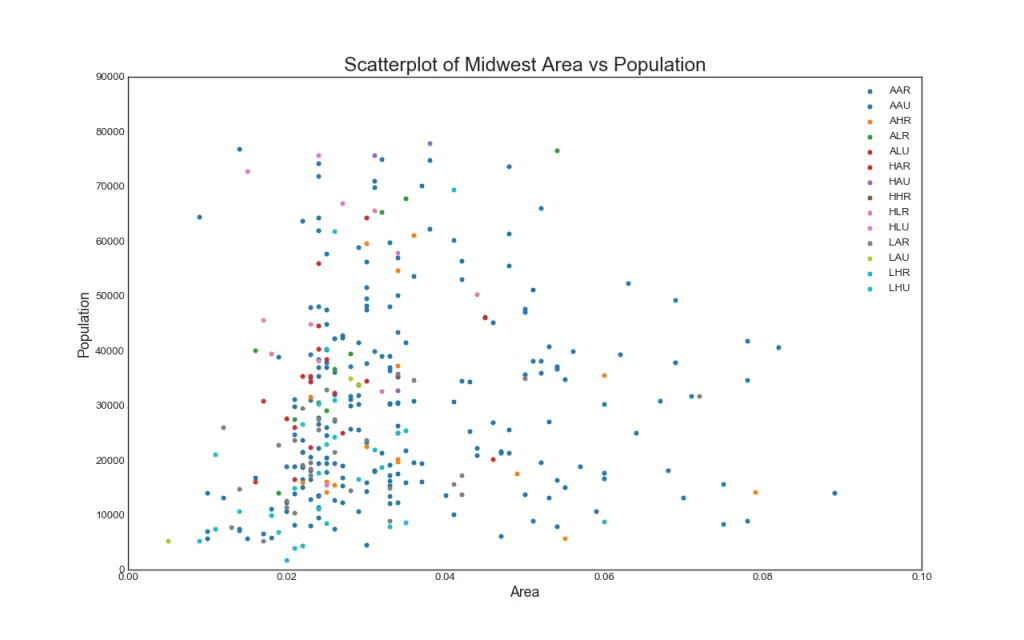
1. Scatter plot
Scatteplot is a classic and fundamental plot used to study the relationship between two variables. If you have multiple groups in your data you may want to visualise each group in a different color. In matplotlib, you can conveniently do this using plt.scatterplot().
# Import dataset
midwest = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/midwest_filter.csv")
# Prepare Data
# Create as many colors as there are unique midwest['category']
categories = np.unique(midwest['category'])
colors = [plt.cm.tab10(i/float(len(categories)-1)) for i in range(len(categories))]
# Draw Plot for Each Category
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
for i, category in enumerate(categories):
plt.scatter('area', 'poptotal',
data=midwest.loc[midwest.category==category, :],
s=20, c=colors[i], label=str(category))
# Decorations
plt.gca().set(xlim=(0.0, 0.1), ylim=(0, 90000),
xlabel='Area', ylabel='Population')
plt.xticks(fontsize=12); plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.title("Scatterplot of Midwest Area vs Population", fontsize=22)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
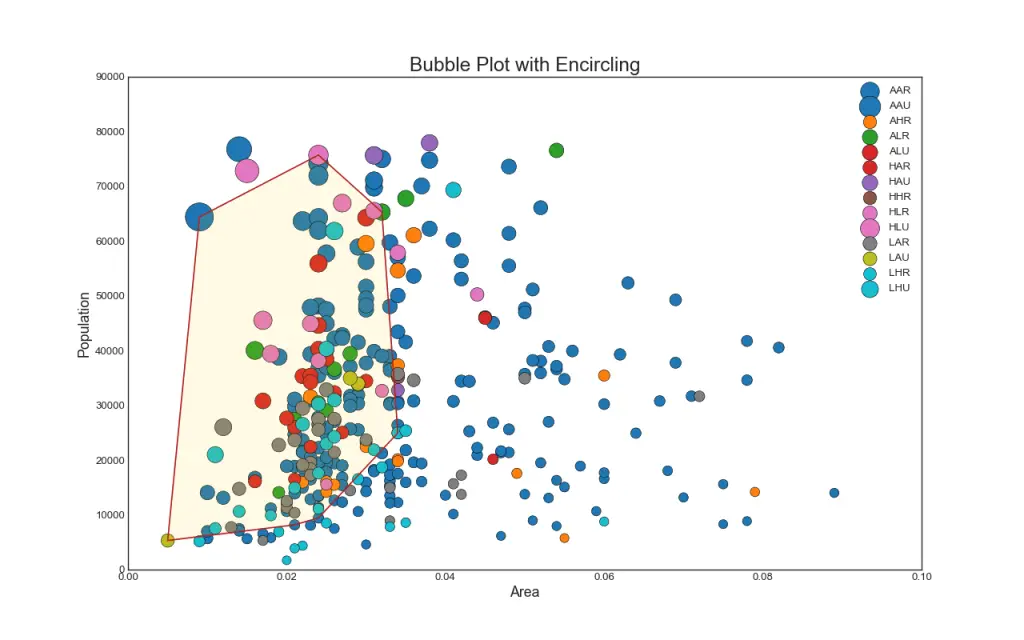
2. Bubble plot with Encircling
Sometimes you want to show a group of points within a boundary to emphasize their importance. In this example, you get the records from the dataframe that should be encircled and pass it to the encircle() described in the code below.
from matplotlib import patches
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
import warnings; warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
sns.set_style("white")
# Step 1: Prepare Data
midwest = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/midwest_filter.csv")
# As many colors as there are unique midwest['category']
categories = np.unique(midwest['category'])
colors = [plt.cm.tab10(i/float(len(categories)-1)) for i in range(len(categories))]
# Step 2: Draw Scatterplot with unique color for each category
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
for i, category in enumerate(categories):
plt.scatter('area', 'poptotal', data=midwest.loc[midwest.category==category, :], s='dot_size', c=colors[i], label=str(category), edgecolors='black', linewidths=.5)
# Step 3: Encircling
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44575681/how-do-i-encircle-different-data-sets-in-scatter-plot
def encircle(x,y, ax=None, **kw):
if not ax: ax=plt.gca()
p = np.c_[x,y]
hull = ConvexHull(p)
poly = plt.Polygon(p[hull.vertices,:], **kw)
ax.add_patch(poly)
# Select data to be encircled
midwest_encircle_data = midwest.loc[midwest.state=='IN', :]
# Draw polygon surrounding vertices
encircle(midwest_encircle_data.area, midwest_encircle_data.poptotal, ec="k", fc="gold", alpha=0.1)
encircle(midwest_encircle_data.area, midwest_encircle_data.poptotal, ec="firebrick", fc="none", linewidth=1.5)
# Step 4: Decorations
plt.gca().set(xlim=(0.0, 0.1), ylim=(0, 90000),
xlabel='Area', ylabel='Population')
plt.xticks(fontsize=12); plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.title("Bubble Plot with Encircling", fontsize=22)
plt.legend(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
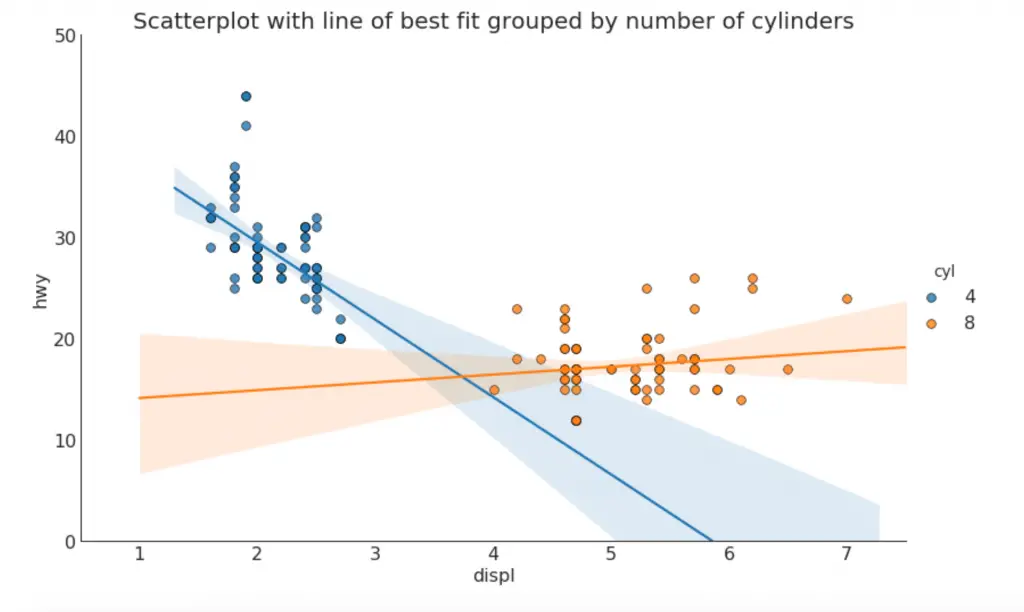
3. Scatter plot with linear regression line of best fit
If you want to understand how two variables change with respect to each other, the line of best fit is the way to go. The below plot shows how the line of best fit differs amongst various groups in the data. To disable the groupings and to just draw one line-of-best-fit for the entire dataset, remove the hue='cyl' parameter from the sns.lmplot() call below.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df_select = df.loc[df.cyl.isin([4,8]), :]
# Plot
sns.set_style("white")
gridobj = sns.lmplot(x="displ", y="hwy", hue="cyl", data=df_select,
height=7, aspect=1.6, robust=True, palette='tab10',
scatter_kws=dict(s=60, linewidths=.7, edgecolors='black'))
# Decorations
gridobj.set(xlim=(0.5, 7.5), ylim=(0, 50))
plt.title("Scatterplot with line of best fit grouped by number of cylinders", fontsize=20)
plt.show()
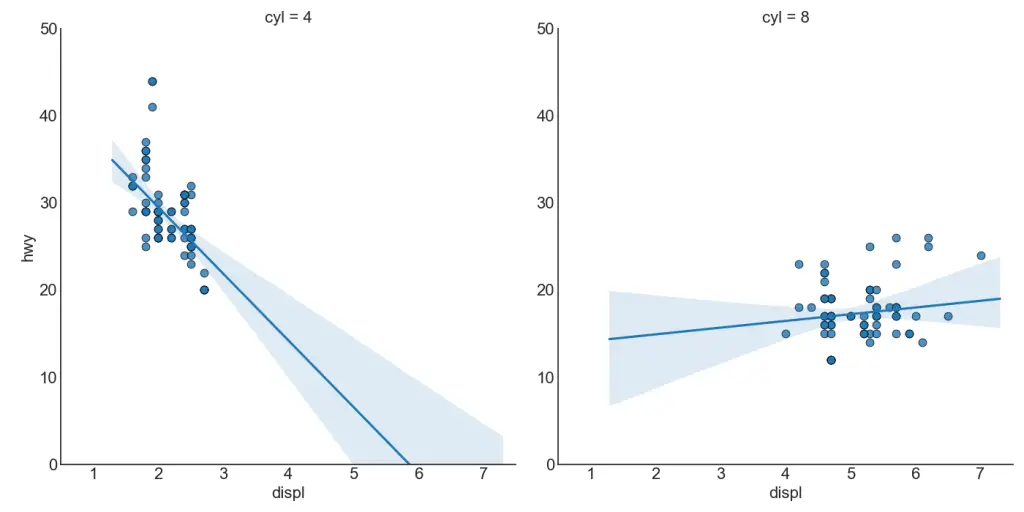
Each regression line in its own column
Alternately, you can show the best fit line for each group in its own column. You cando this by setting the col=groupingcolumn parameter inside the sns.lmplot().
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df_select = df.loc[df.cyl.isin([4,8]), :]
# Each line in its own column
sns.set_style("white")
gridobj = sns.lmplot(x="displ", y="hwy",
data=df_select,
height=7,
robust=True,
palette='Set1',
col="cyl",
scatter_kws=dict(s=60, linewidths=.7, edgecolors='black'))
# Decorations
gridobj.set(xlim=(0.5, 7.5), ylim=(0, 50))
plt.show()
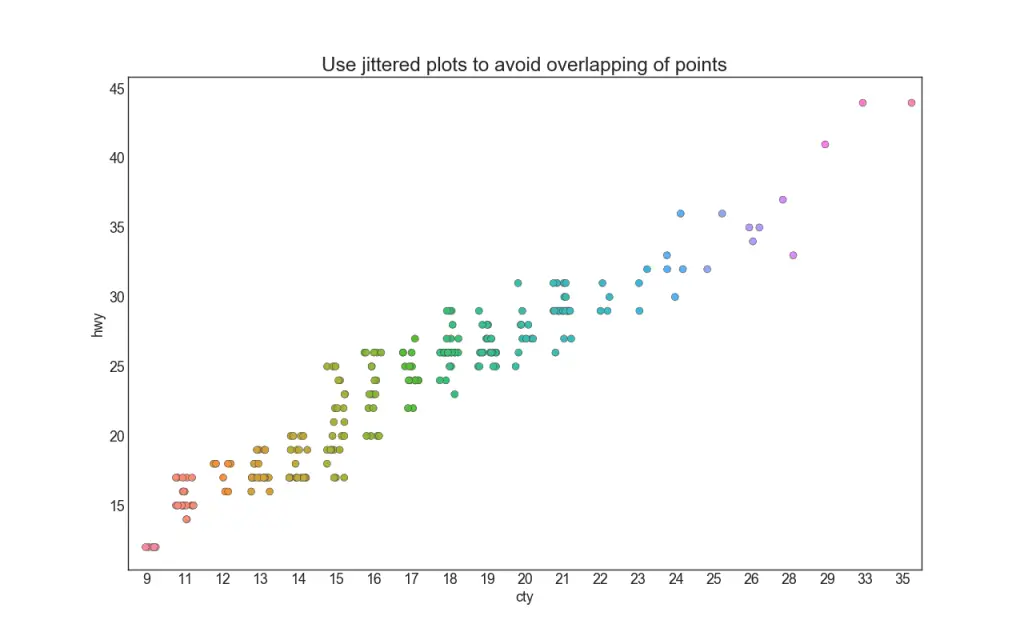
4. Jittering with stripplot
Often multiple datapoints have exactly the same X and Y values. As a result, multiple points get plotted over each other and hide. To avoid this, jitter the points slightly so you can visually see them. This is convenient to do using seaborn’s stripplot().
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Stripplot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
sns.stripplot(df.cty, df.hwy, jitter=0.25, size=8, ax=ax, linewidth=.5)
# Decorations
plt.title('Use jittered plots to avoid overlapping of points', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
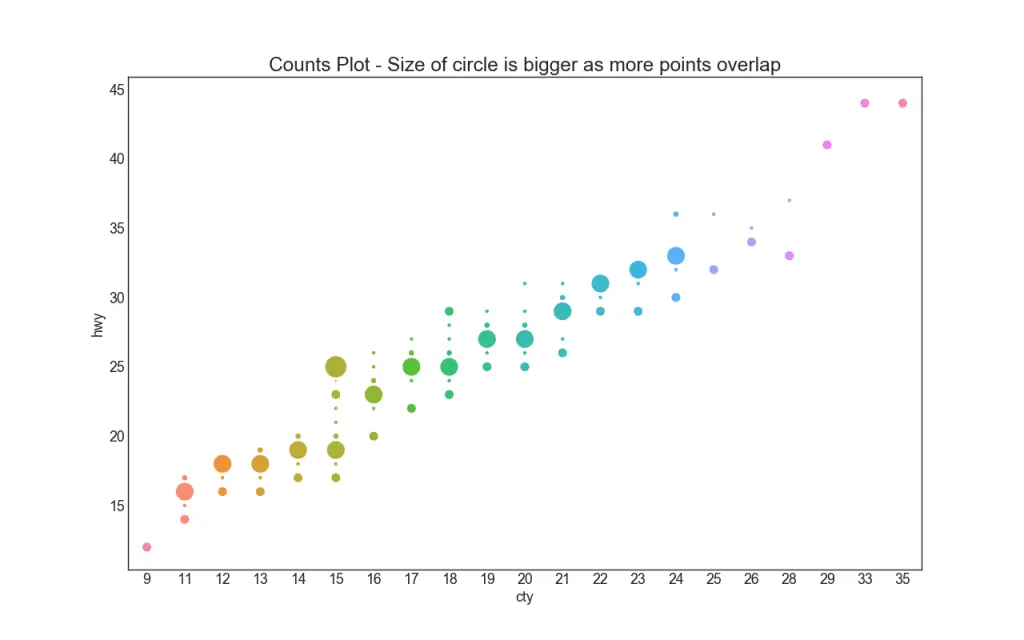
5. Counts Plot
Another option to avoid the problem of points overlap is the increase the size of the dot depending on how many points lie in that spot. So, larger the size of the point more is the concentration of points around that.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df_counts = df.groupby(['hwy', 'cty']).size().reset_index(name='counts')
# Draw Stripplot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
sns.stripplot(df_counts.cty, df_counts.hwy, size=df_counts.counts*2, ax=ax)
# Decorations
plt.title('Counts Plot - Size of circle is bigger as more points overlap', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
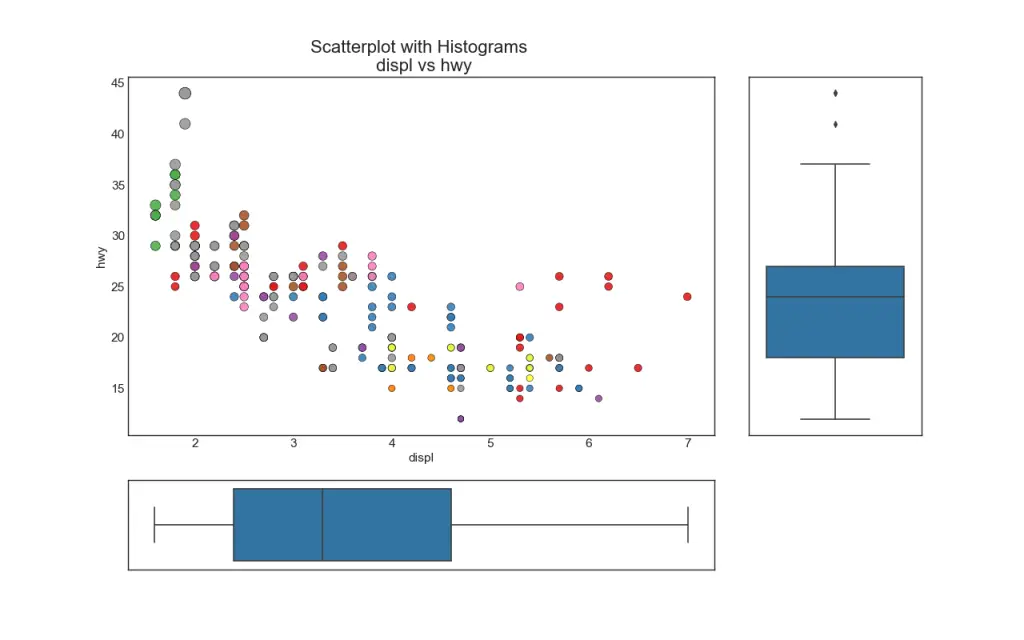
6. Marginal Histogram
Marginal histograms have a histogram along the X and Y axis variables. This is used to visualize the relationship between the X and Y along with the univariate distribution of the X and the Y individually. This plot if often used in exploratory data analysis (EDA).
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Create Fig and gridspec
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80)
grid = plt.GridSpec(4, 4, hspace=0.5, wspace=0.2)
# Define the axes
ax_main = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, :-1])
ax_right = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, -1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
ax_bottom = fig.add_subplot(grid[-1, 0:-1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
# Scatterplot on main ax
ax_main.scatter('displ', 'hwy', s=df.cty*4, c=df.manufacturer.astype('category').cat.codes, alpha=.9, data=df, cmap="tab10", edgecolors='gray', linewidths=.5)
# histogram on the right
ax_bottom.hist(df.displ, 40, histtype='stepfilled', orientation='vertical', color='deeppink')
ax_bottom.invert_yaxis()
# histogram in the bottom
ax_right.hist(df.hwy, 40, histtype='stepfilled', orientation='horizontal', color='deeppink')
# Decorations
ax_main.set(title='Scatterplot with Histograms \n displ vs hwy', xlabel='displ', ylabel='hwy')
ax_main.title.set_fontsize(20)
for item in ([ax_main.xaxis.label, ax_main.yaxis.label] + ax_main.get_xticklabels() + ax_main.get_yticklabels()):
item.set_fontsize(14)
xlabels = ax_main.get_xticks().tolist()
ax_main.set_xticklabels(xlabels)
plt.show()
7. Marginal Boxplot
Marginal boxplot serves a similar purpose as marginal histogram. However, the boxplot helps to pinpoint the median, 25th and 75th percentiles of the X and the Y.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Create Fig and gridspec
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80)
grid = plt.GridSpec(4, 4, hspace=0.5, wspace=0.2)
# Define the axes
ax_main = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, :-1])
ax_right = fig.add_subplot(grid[:-1, -1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
ax_bottom = fig.add_subplot(grid[-1, 0:-1], xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[])
# Scatterplot on main ax
ax_main.scatter('displ', 'hwy', s=df.cty*5, c=df.manufacturer.astype('category').cat.codes, alpha=.9, data=df, cmap="Set1", edgecolors='black', linewidths=.5)
# Add a graph in each part
sns.boxplot(df.hwy, ax=ax_right, orient="v")
sns.boxplot(df.displ, ax=ax_bottom, orient="h")
# Decorations ------------------
# Remove x axis name for the boxplot
ax_bottom.set(xlabel='')
ax_right.set(ylabel='')
# Main Title, Xlabel and YLabel
ax_main.set(title='Scatterplot with Histograms \n displ vs hwy', xlabel='displ', ylabel='hwy')
# Set font size of different components
ax_main.title.set_fontsize(20)
for item in ([ax_main.xaxis.label, ax_main.yaxis.label] + ax_main.get_xticklabels() + ax_main.get_yticklabels()):
item.set_fontsize(14)
plt.show()
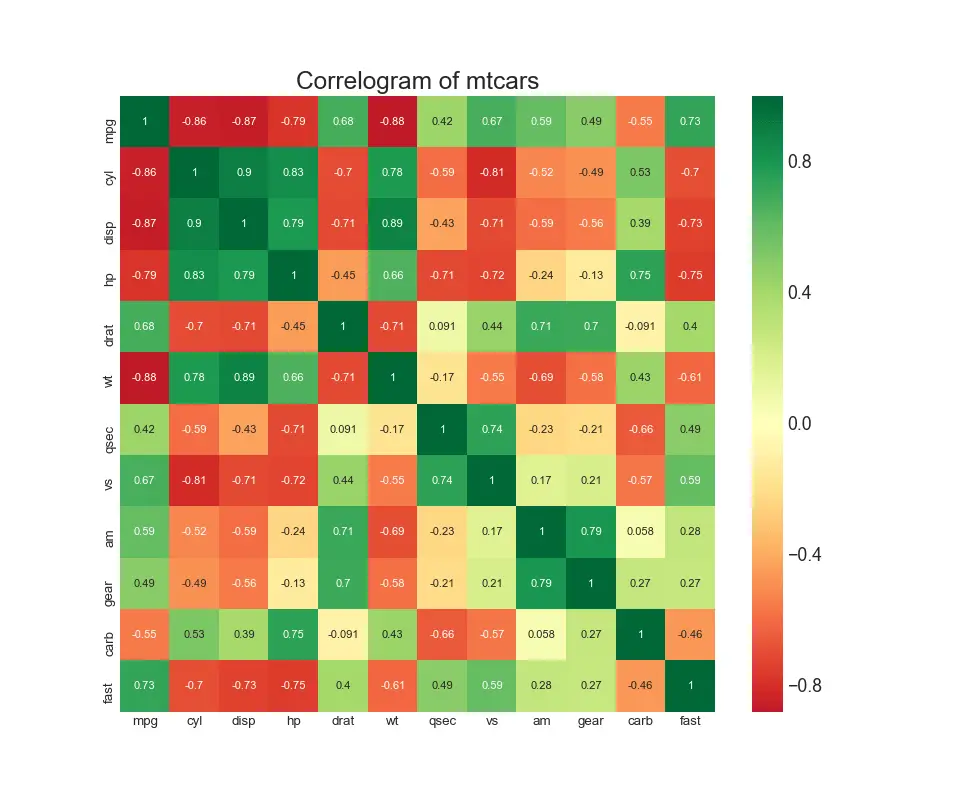
8. Correllogram
Correlogram is used to visually see the correlation metric between all possible pairs of numeric variables in a given dataframe (or 2D array).
# Import Dataset
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(12,10), dpi= 80)
sns.heatmap(df.corr(), xticklabels=df.corr().columns, yticklabels=df.corr().columns, cmap='RdYlGn', center=0, annot=True)
# Decorations
plt.title('Correlogram of mtcars', fontsize=22)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
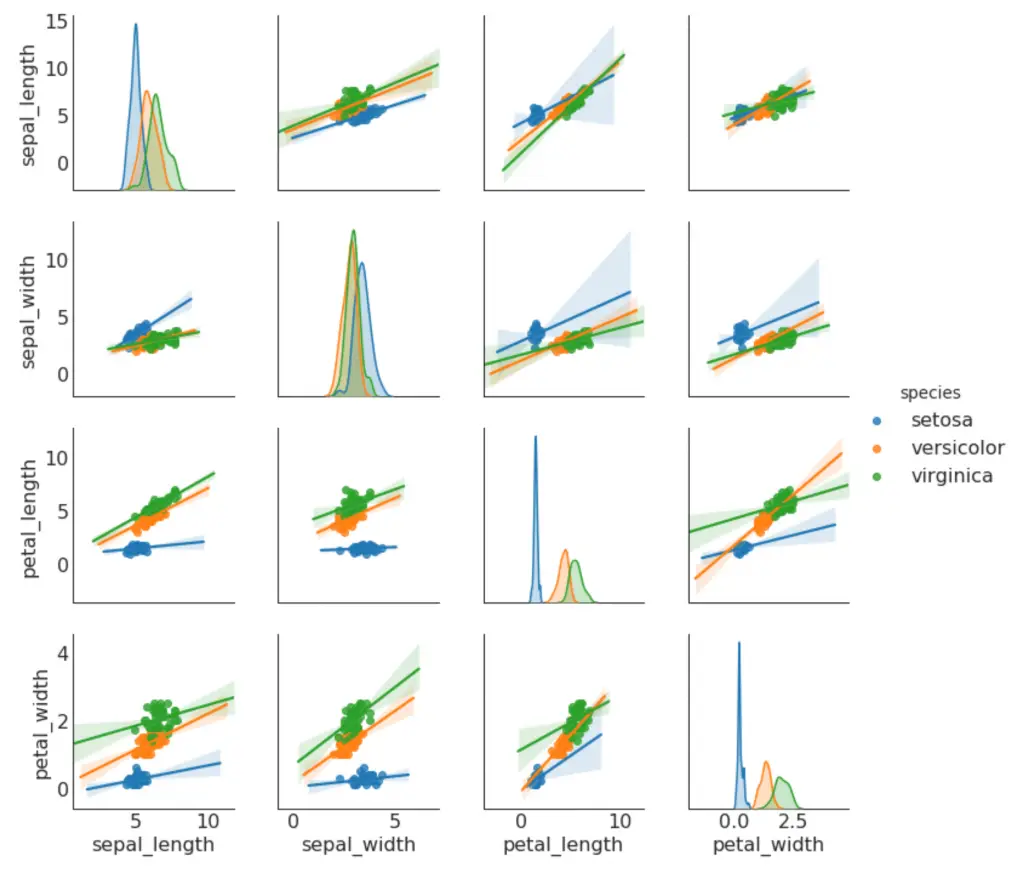
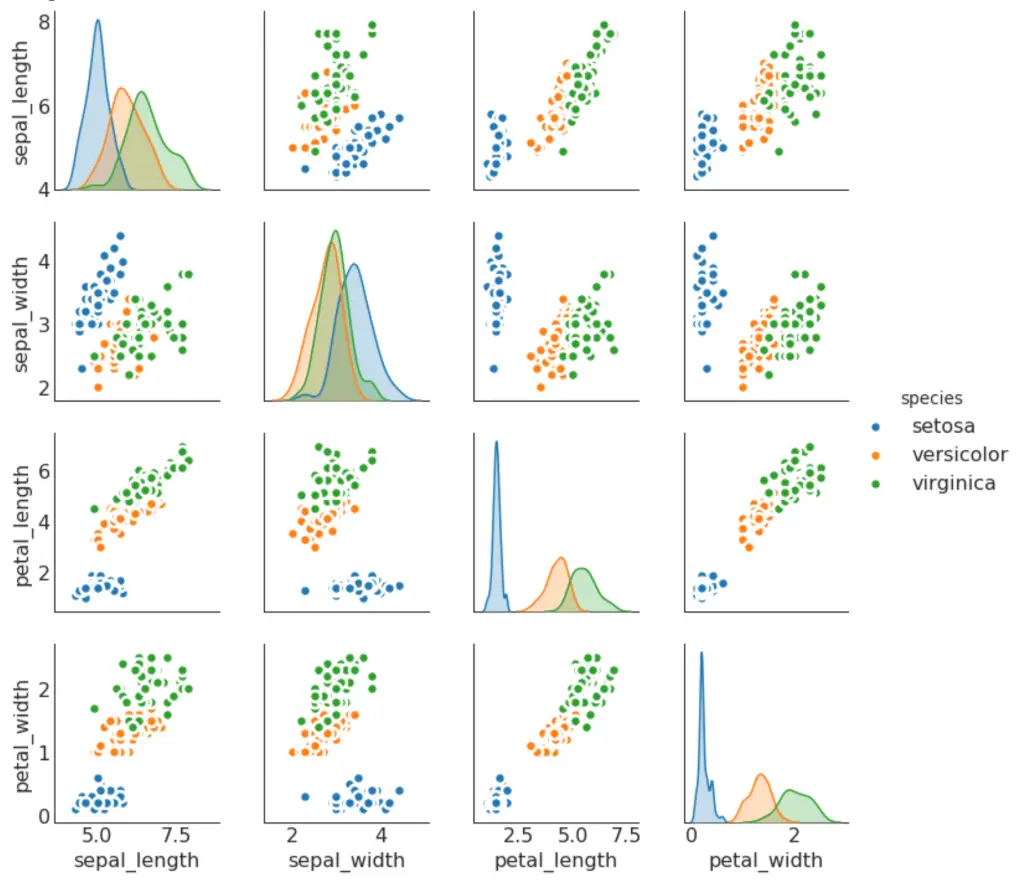
9. Pairwise Plot
Pairwise plot is a favorite in exploratory analysis to understand the relationship between all possible pairs of numeric variables. It is a must have tool for bivariate analysis.
# Load Dataset
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8), dpi= 80)
sns.pairplot(df, kind="scatter", hue="species", plot_kws=dict(s=80, edgecolor="white", linewidth=2.5))
plt.show()
# Load Dataset
df = sns.load_dataset('iris')
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8), dpi= 80)
sns.pairplot(df, kind="reg", hue="species")
plt.show()
Deviation
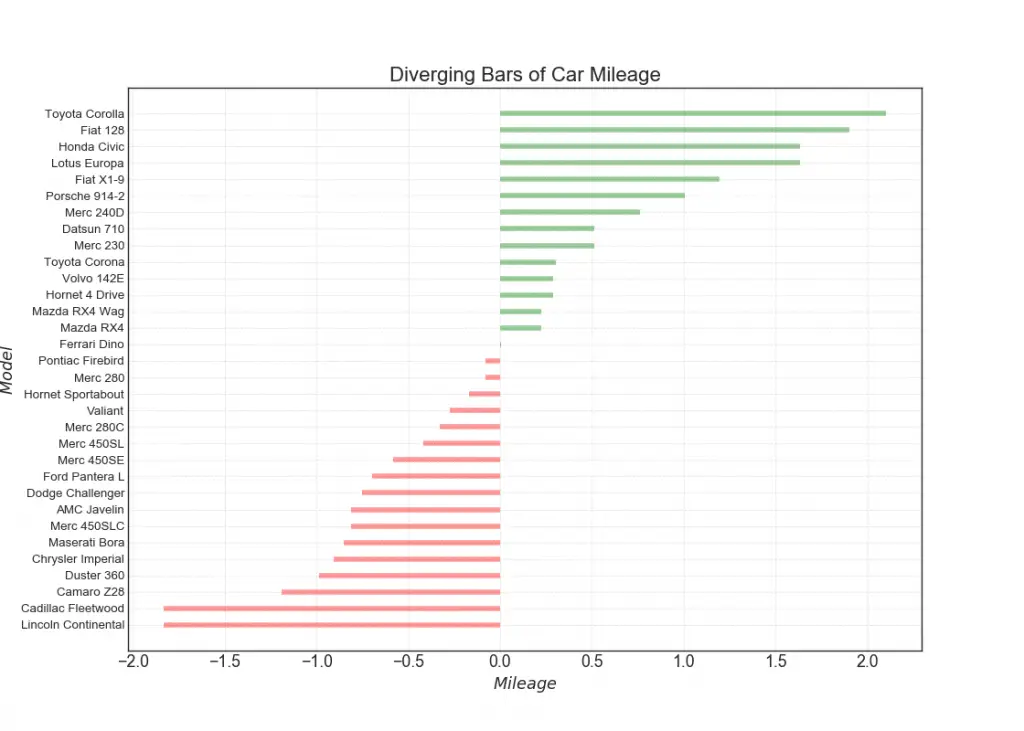
10. Diverging Bars
If you want to see how the items are varying based on a single metric and visualize the order and amount of this variance, the diverging bars is a great tool. It helps to quickly differentiate the performance of groups in your data and is quite intuitive and instantly conveys the point.
# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
x = df.loc[:, ['mpg']]
df['mpg_z'] = (x - x.mean())/x.std()
df['colors'] = ['red' if x < 0 else 'green' for x in df['mpg_z']]
df.sort_values('mpg_z', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
plt.figure(figsize=(14,10), dpi= 80)
plt.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=0, xmax=df.mpg_z, color=df.colors, alpha=0.4, linewidth=5)
# Decorations
plt.gca().set(ylabel='$Model$', xlabel='$Mileage$')
plt.yticks(df.index, df.cars, fontsize=12)
plt.title('Diverging Bars of Car Mileage', fontdict={'size':20})
plt.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
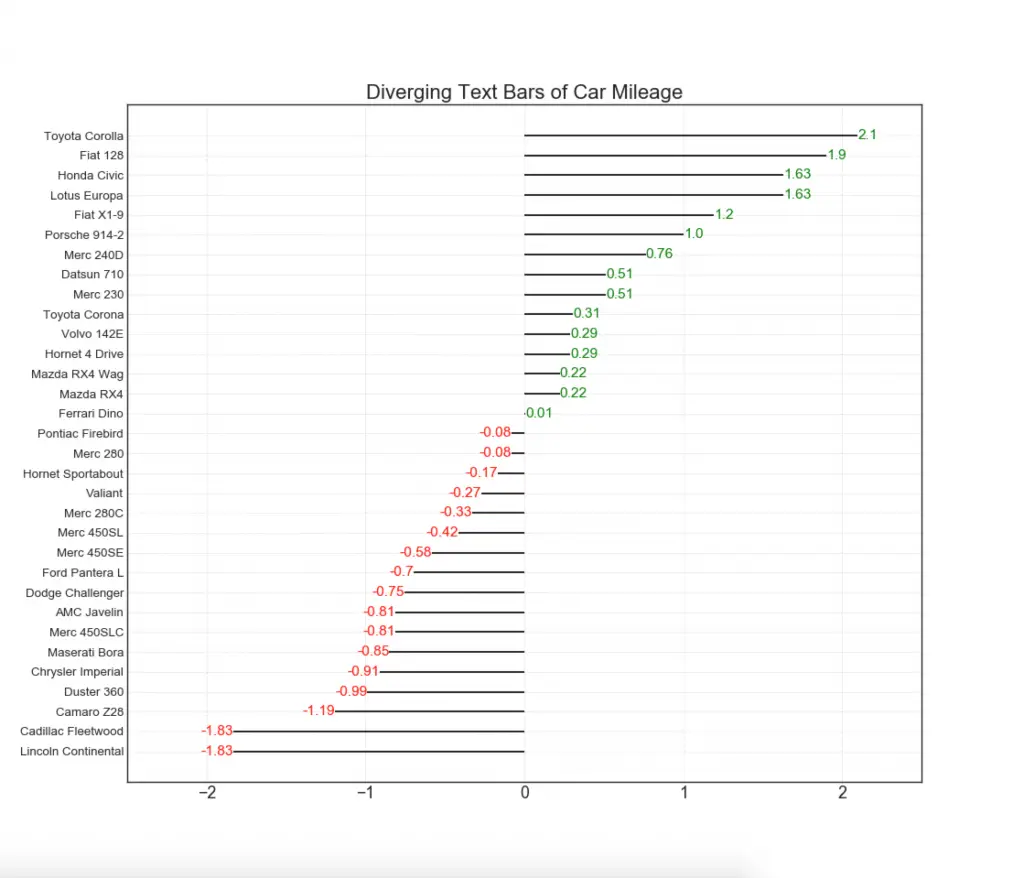
11. Diverging Texts
Diverging texts is similar to diverging bars and it preferred if you want to show the value of each items within the chart in a nice and presentable way.
# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
x = df.loc[:, ['mpg']]
df['mpg_z'] = (x - x.mean())/x.std()
df['colors'] = ['red' if x < 0 else 'green' for x in df['mpg_z']]
df.sort_values('mpg_z', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
plt.figure(figsize=(14,14), dpi= 80)
plt.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=0, xmax=df.mpg_z)
for x, y, tex in zip(df.mpg_z, df.index, df.mpg_z):
t = plt.text(x, y, round(tex, 2), horizontalalignment='right' if x < 0 else 'left',
verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'color':'red' if x < 0 else 'green', 'size':14})
# Decorations
plt.yticks(df.index, df.cars, fontsize=12)
plt.title('Diverging Text Bars of Car Mileage', fontdict={'size':20})
plt.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.xlim(-2.5, 2.5)
plt.show()
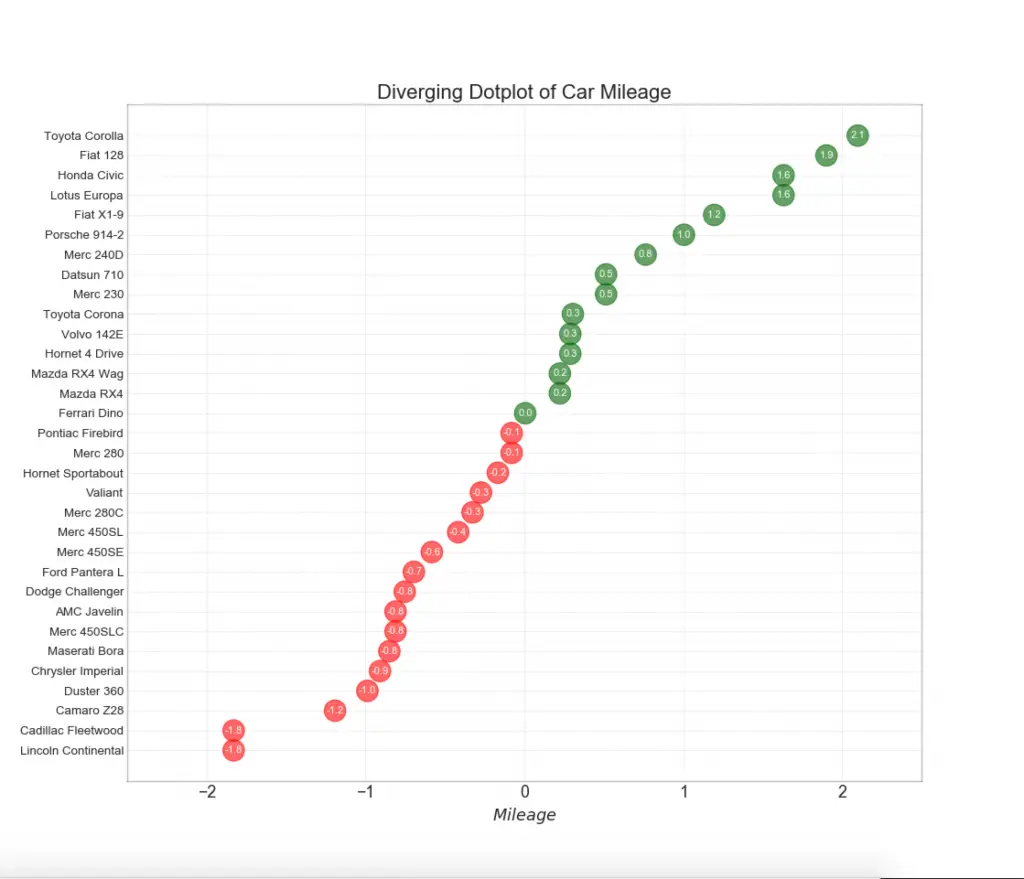
12. Diverging Dot Plot
Divering dot plot is also similar to the diverging bars. However compared to diverging bars, the absence of bars reduces the amount of contrast and disparity between the groups.
Show Code# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
x = df.loc[:, ['mpg']]
df['mpg_z'] = (x - x.mean())/x.std()
df['colors'] = ['red' if x < 0 else 'darkgreen' for x in df['mpg_z']]
df.sort_values('mpg_z', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
plt.figure(figsize=(14,16), dpi= 80)
plt.scatter(df.mpg_z, df.index, s=450, alpha=.6, color=df.colors)
for x, y, tex in zip(df.mpg_z, df.index, df.mpg_z):
t = plt.text(x, y, round(tex, 1), horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'color':'white'})
# Decorations
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.yticks(df.index, df.cars)
plt.title('Diverging Dotplot of Car Mileage', fontdict={'size':20})
plt.xlabel('$Mileage$')
plt.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.xlim(-2.5, 2.5)
plt.show()
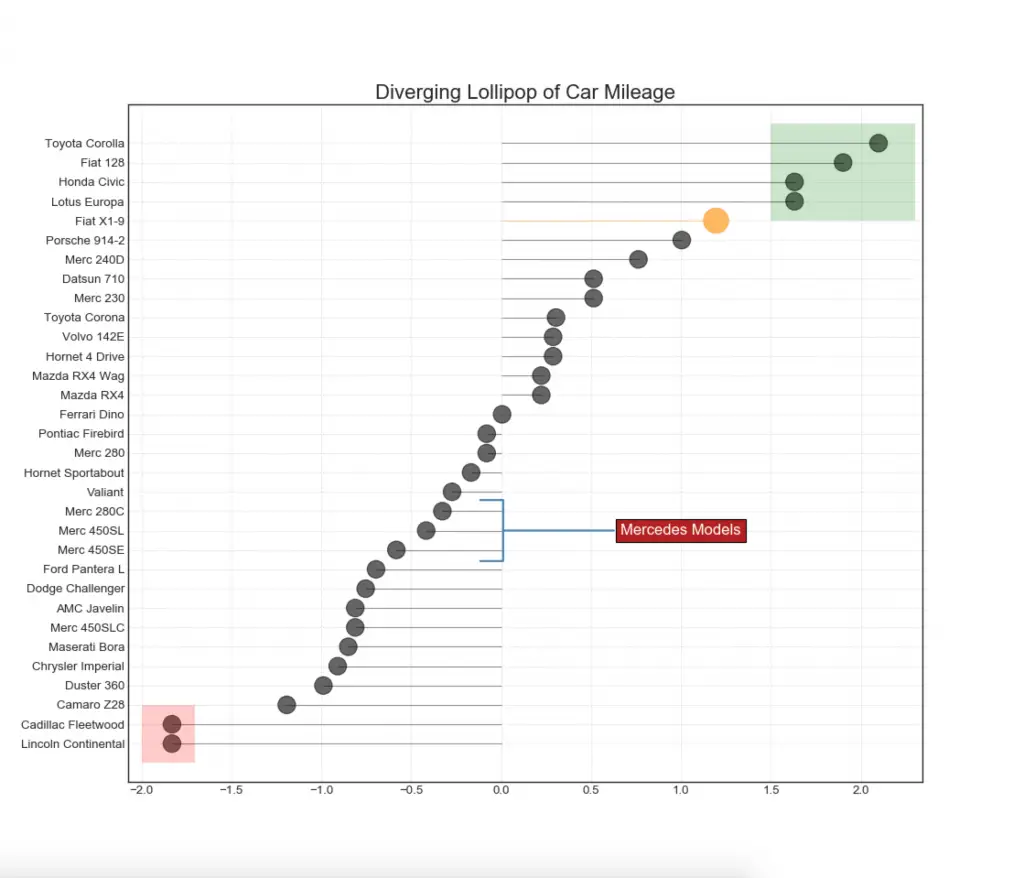
13. Diverging Lollipop Chart with Markers
Lollipop with markers provides a flexible way of visualizing the divergence by laying emphasis on any significant datapoints you want to bring attention to and give reasoning within the chart appropriately.
Show Code# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
x = df.loc[:, ['mpg']]
df['mpg_z'] = (x - x.mean())/x.std()
df['colors'] = 'black'
# color fiat differently
df.loc[df.cars == 'Fiat X1-9', 'colors'] = 'darkorange'
df.sort_values('mpg_z', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
import matplotlib.patches as patches
plt.figure(figsize=(14,16), dpi= 80)
plt.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=0, xmax=df.mpg_z, color=df.colors, alpha=0.4, linewidth=1)
plt.scatter(df.mpg_z, df.index, color=df.colors, s=[600 if x == 'Fiat X1-9' else 300 for x in df.cars], alpha=0.6)
plt.yticks(df.index, df.cars)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
# Annotate
plt.annotate('Mercedes Models', xy=(0.0, 11.0), xytext=(1.0, 11), xycoords='data',
fontsize=15, ha='center', va='center',
bbox=dict(boxstyle='square', fc='firebrick'),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='-[, widthB=2.0, lengthB=1.5', lw=2.0, color='steelblue'), color='white')
# Add Patches
p1 = patches.Rectangle((-2.0, -1), width=.3, height=3, alpha=.2, facecolor='red')
p2 = patches.Rectangle((1.5, 27), width=.8, height=5, alpha=.2, facecolor='green')
plt.gca().add_patch(p1)
plt.gca().add_patch(p2)
# Decorate
plt.title('Diverging Bars of Car Mileage', fontdict={'size':20})
plt.grid(linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
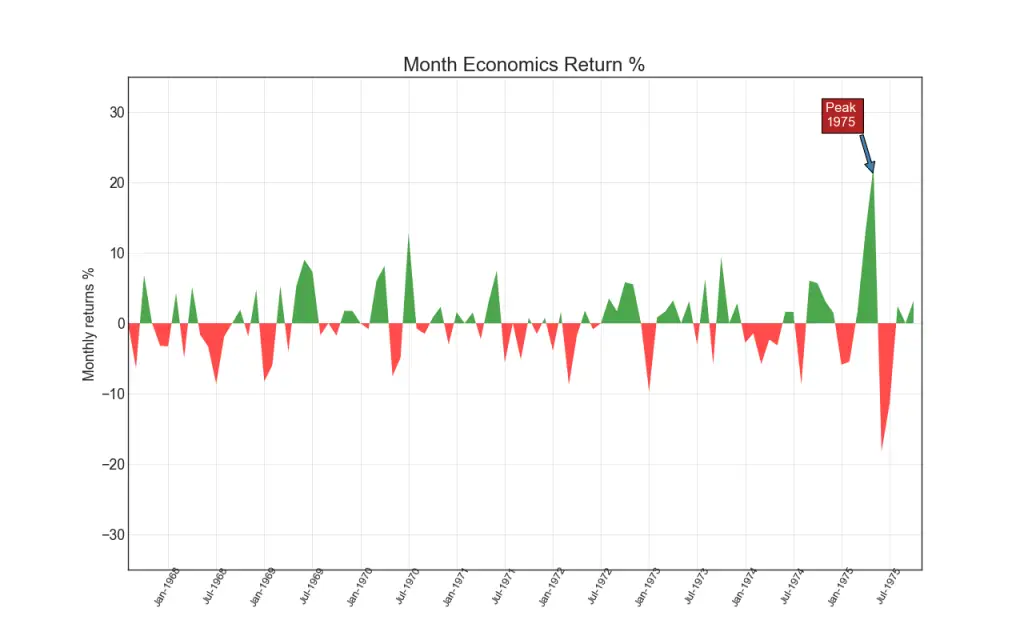
14. Area Chart
By coloring the area between the axis and the lines, the area chart throws more emphasis not just on the peaks and troughs but also the duration of the highs and lows. The longer the duration of the highs, the larger is the area under the line.
Show Codeimport numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Prepare Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/economics.csv", parse_dates=['date']).head(100)
x = np.arange(df.shape[0])
y_returns = (df.psavert.diff().fillna(0)/df.psavert.shift(1)).fillna(0) * 100
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
plt.fill_between(x[1:], y_returns[1:], 0, where=y_returns[1:] >= 0, facecolor='green', interpolate=True, alpha=0.7)
plt.fill_between(x[1:], y_returns[1:], 0, where=y_returns[1:] <= 0, facecolor='red', interpolate=True, alpha=0.7)
# Annotate
plt.annotate('Peak \n1975', xy=(94.0, 21.0), xytext=(88.0, 28),
bbox=dict(boxstyle='square', fc='firebrick'),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='steelblue', shrink=0.05), fontsize=15, color='white')
# Decorations
xtickvals = [str(m)[:3].upper()+"-"+str(y) for y,m in zip(df.date.dt.year, df.date.dt.month_name())]
plt.gca().set_xticks(x[::6])
plt.gca().set_xticklabels(xtickvals[::6], rotation=90, fontdict={'horizontalalignment': 'center', 'verticalalignment': 'center_baseline'})
plt.ylim(-35,35)
plt.xlim(1,100)
plt.title("Month Economics Return %", fontsize=22)
plt.ylabel('Monthly returns %')
plt.grid(alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
Ranking
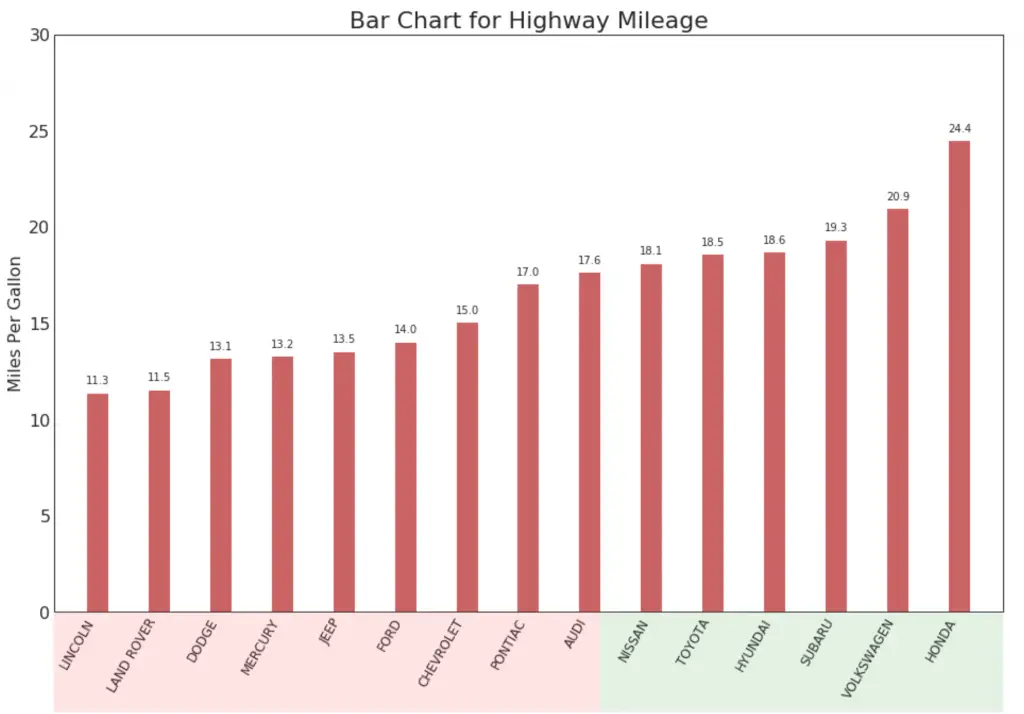
15. Ordered Bar Chart
Ordered bar chart conveys the rank order of the items effectively. But adding the value of the metric above the chart, the user gets the precise information from the chart itself. It is a classic way of visualizing items based on counts or any given metric. Check this free video tutorial on implementing and interpreting ordered bar charts.
Show Code# Prepare Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.mean())
df.sort_values('cty', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
import matplotlib.patches as patches
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), facecolor='white', dpi= 80)
ax.vlines(x=df.index, ymin=0, ymax=df.cty, color='firebrick', alpha=0.7, linewidth=20)
# Annotate Text
for i, cty in enumerate(df.cty):
ax.text(i, cty+0.5, round(cty, 1), horizontalalignment='center')
# Title, Label, Ticks and Ylim
ax.set_title('Bar Chart for Highway Mileage', fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set(ylabel='Miles Per Gallon', ylim=(0, 30))
plt.xticks(df.index, df.manufacturer.str.upper(), rotation=60, horizontalalignment='right', fontsize=12)
# Add patches to color the X axis labels
p1 = patches.Rectangle((.57, -0.005), width=.33, height=.13, alpha=.1, facecolor='green', transform=fig.transFigure)
p2 = patches.Rectangle((.124, -0.005), width=.446, height=.13, alpha=.1, facecolor='red', transform=fig.transFigure)
fig.add_artist(p1)
fig.add_artist(p2)
plt.show()
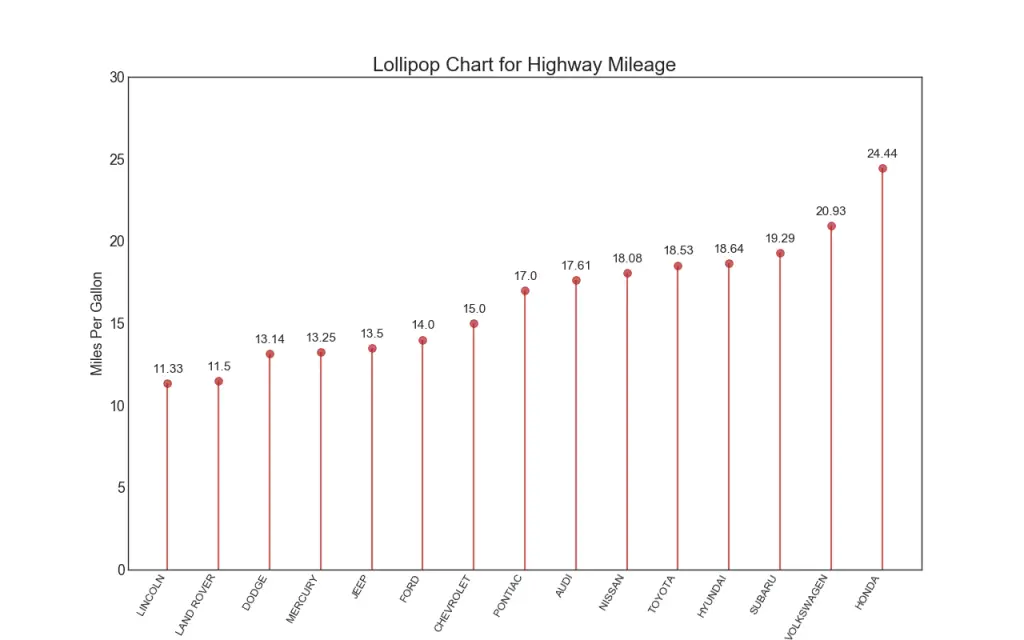
16. Lollipop Chart
Lollipop chart serves a similar purpose as a ordered bar chart in a visually pleasing way.
Show Code# Prepare Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.mean())
df.sort_values('cty', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
ax.vlines(x=df.index, ymin=0, ymax=df.cty, color='firebrick', alpha=0.7, linewidth=2)
ax.scatter(x=df.index, y=df.cty, s=75, color='firebrick', alpha=0.7)
# Title, Label, Ticks and Ylim
ax.set_title('Lollipop Chart for Highway Mileage', fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set_ylabel('Miles Per Gallon')
ax.set_xticks(df.index)
ax.set_xticklabels(df.manufacturer.str.upper(), rotation=60, fontdict={'horizontalalignment': 'right', 'size':12})
ax.set_ylim(0, 30)
# Annotate
for row in df.itertuples():
ax.text(row.Index, row.cty+.5, s=round(row.cty, 2), horizontalalignment= 'center', verticalalignment='bottom', fontsize=14)
plt.show()
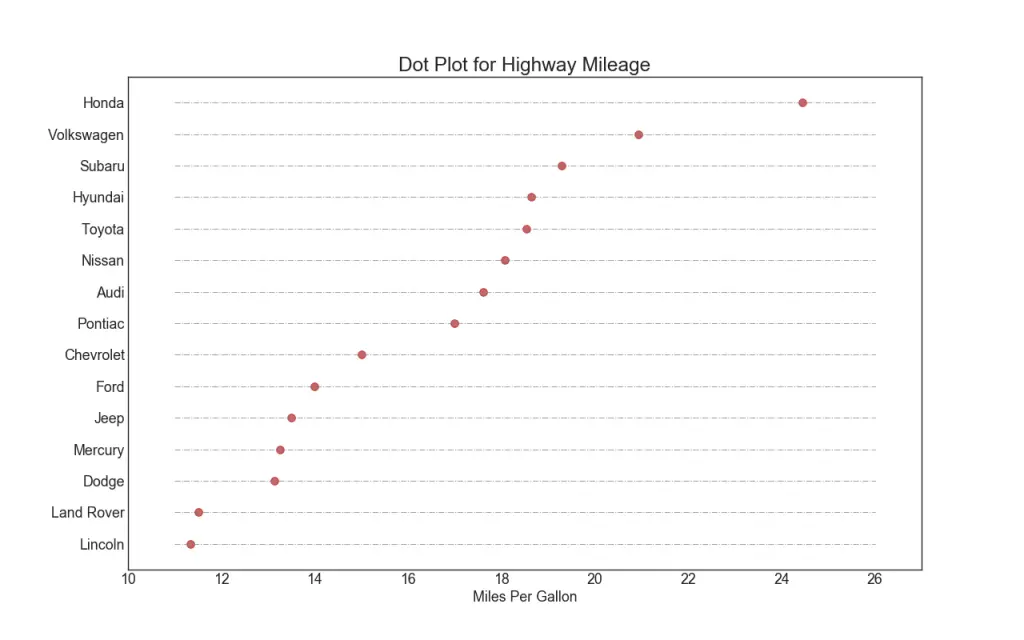
17. Dot Plot
The dot plot conveys the rank order of the items. And since it is aligned along the horizontal axis, you can visualize how far the points are from each other more easily.
# Prepare Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
df = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.mean())
df.sort_values('cty', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Draw plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
ax.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=11, xmax=26, color='gray', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1, linestyles='dashdot')
ax.scatter(y=df.index, x=df.cty, s=75, color='firebrick', alpha=0.7)
# Title, Label, Ticks and Ylim
ax.set_title('Dot Plot for Highway Mileage', fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set_xlabel('Miles Per Gallon')
ax.set_yticks(df.index)
ax.set_yticklabels(df.manufacturer.str.title(), fontdict={'horizontalalignment': 'right'})
ax.set_xlim(10, 27)
plt.show()
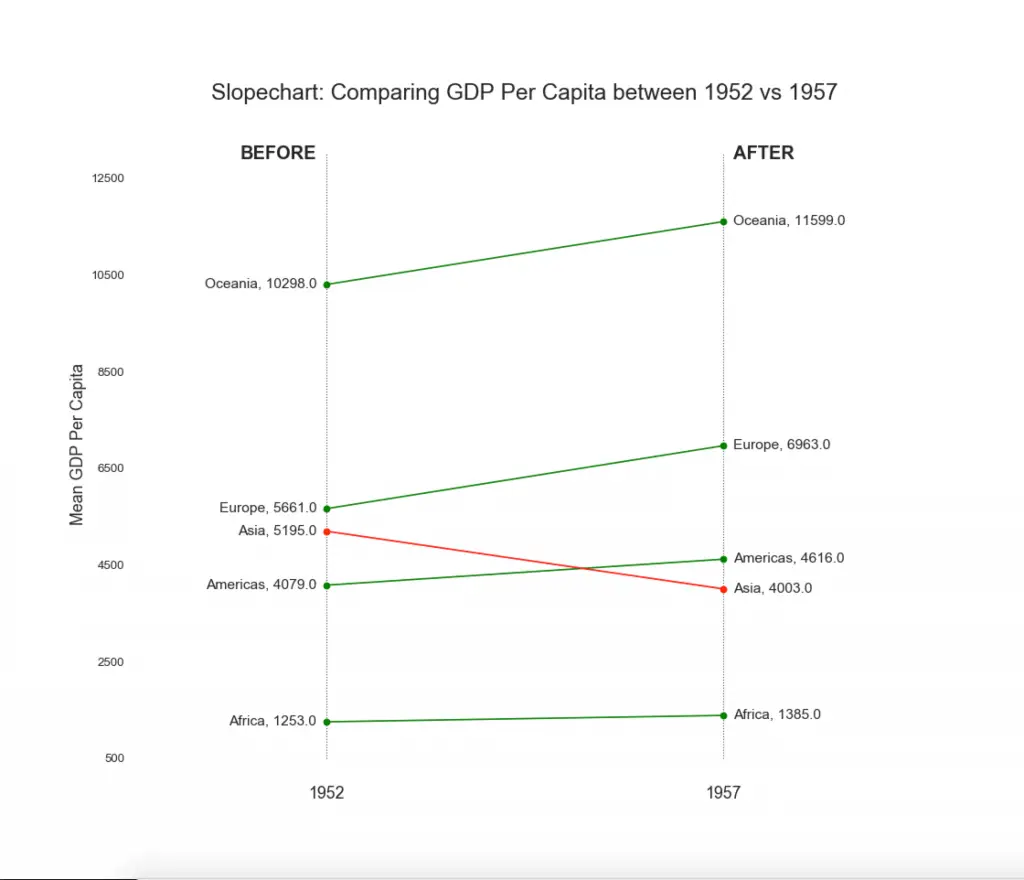
18. Slope Chart
Slope chart is most suitable for comparing the ‘Before’ and ‘After’ positions of a given person/item.
Show Codeimport matplotlib.lines as mlines
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/gdppercap.csv")
left_label = [str(c) + ', '+ str(round(y)) for c, y in zip(df.continent, df['1952'])]
right_label = [str(c) + ', '+ str(round(y)) for c, y in zip(df.continent, df['1957'])]
klass = ['red' if (y1-y2) < 0 else 'green' for y1, y2 in zip(df['1952'], df['1957'])]
# draw line
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/36470343/how-to-draw-a-line-with-matplotlib/36479941
def newline(p1, p2, color='black'):
ax = plt.gca()
l = mlines.Line2D([p1[0],p2[0]], [p1[1],p2[1]], color='red' if p1[1]-p2[1] > 0 else 'green', marker='o', markersize=6)
ax.add_line(l)
return l
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(14,14), dpi= 80)
# Vertical Lines
ax.vlines(x=1, ymin=500, ymax=13000, color='black', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
ax.vlines(x=3, ymin=500, ymax=13000, color='black', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
# Points
ax.scatter(y=df['1952'], x=np.repeat(1, df.shape[0]), s=10, color='black', alpha=0.7)
ax.scatter(y=df['1957'], x=np.repeat(3, df.shape[0]), s=10, color='black', alpha=0.7)
# Line Segmentsand Annotation
for p1, p2, c in zip(df['1952'], df['1957'], df['continent']):
newline([1,p1], [3,p2])
ax.text(1-0.05, p1, c + ', ' + str(round(p1)), horizontalalignment='right', verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'size':14})
ax.text(3+0.05, p2, c + ', ' + str(round(p2)), horizontalalignment='left', verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'size':14})
# 'Before' and 'After' Annotations
ax.text(1-0.05, 13000, 'BEFORE', horizontalalignment='right', verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'size':18, 'weight':700})
ax.text(3+0.05, 13000, 'AFTER', horizontalalignment='left', verticalalignment='center', fontdict={'size':18, 'weight':700})
# Decoration
ax.set_title("Slopechart: Comparing GDP Per Capita between 1952 vs 1957", fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set(xlim=(0,4), ylim=(0,14000), ylabel='Mean GDP Per Capita')
ax.set_xticks([1,3])
ax.set_xticklabels(["1952", "1957"])
plt.yticks(np.arange(500, 13000, 2000), fontsize=12)
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.show()
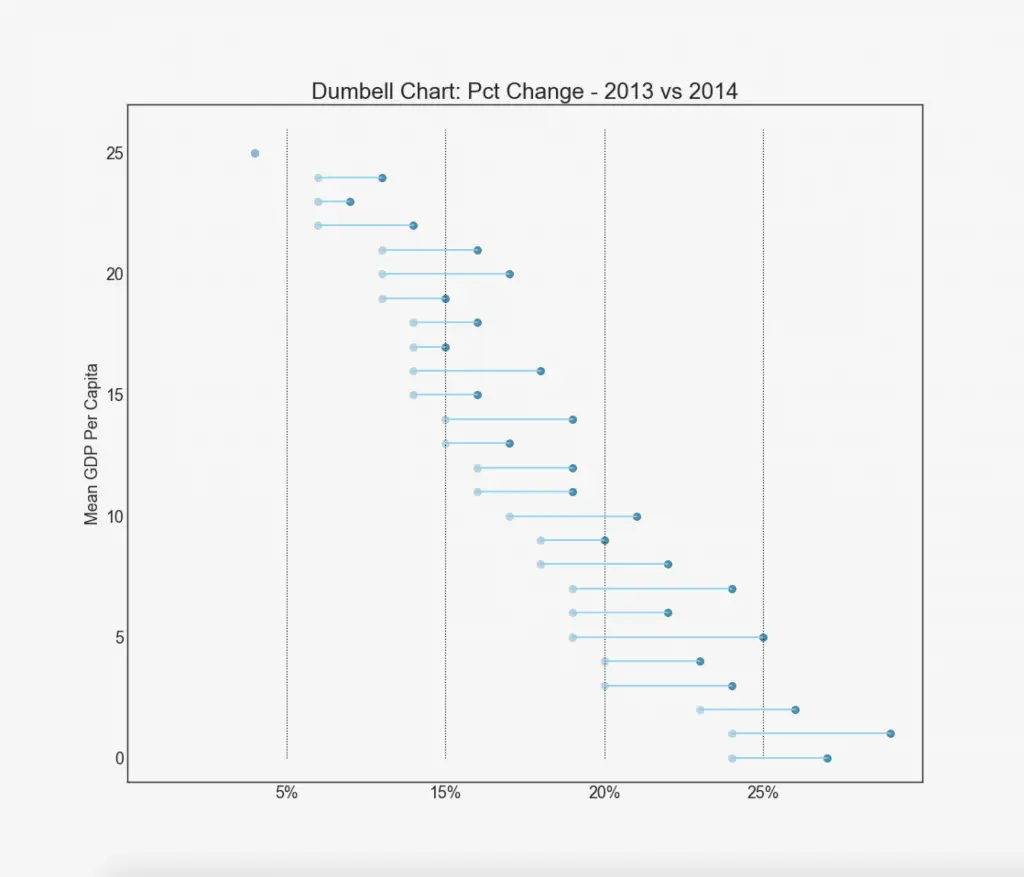
19. Dumbbell Plot
Dumbbell plot conveys the ‘before’ and ‘after’ positions of various items along with the rank ordering of the items. Its very useful if you want to visualize the effect of a particular project / initiative on different objects.
Show Codeimport matplotlib.lines as mlines
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/health.csv")
df.sort_values('pct_2014', inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
# Func to draw line segment
def newline(p1, p2, color='black'):
ax = plt.gca()
l = mlines.Line2D([p1[0],p2[0]], [p1[1],p2[1]], color='skyblue')
ax.add_line(l)
return l
# Figure and Axes
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(14,14), facecolor='#f7f7f7', dpi= 80)
# Vertical Lines
ax.vlines(x=.05, ymin=0, ymax=26, color='black', alpha=1, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
ax.vlines(x=.10, ymin=0, ymax=26, color='black', alpha=1, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
ax.vlines(x=.15, ymin=0, ymax=26, color='black', alpha=1, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
ax.vlines(x=.20, ymin=0, ymax=26, color='black', alpha=1, linewidth=1, linestyles='dotted')
# Points
ax.scatter(y=df['index'], x=df['pct_2013'], s=50, color='#0e668b', alpha=0.7)
ax.scatter(y=df['index'], x=df['pct_2014'], s=50, color='#a3c4dc', alpha=0.7)
# Line Segments
for i, p1, p2 in zip(df['index'], df['pct_2013'], df['pct_2014']):
newline([p1, i], [p2, i])
# Decoration
ax.set_facecolor('#f7f7f7')
ax.set_title("Dumbell Chart: Pct Change - 2013 vs 2014", fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set(xlim=(0,.25), ylim=(-1, 27), ylabel='Mean GDP Per Capita')
ax.set_xticks([.05, .1, .15, .20])
ax.set_xticklabels(['5%', '15%', '20%', '25%'])
ax.set_xticklabels(['5%', '15%', '20%', '25%'])
plt.show()
Distribution
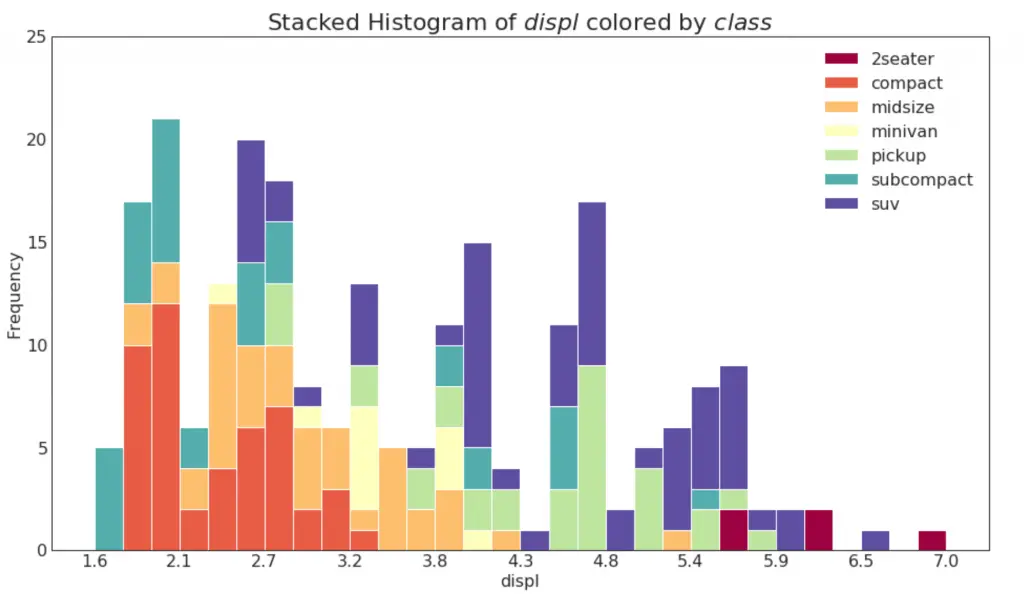
20. Histogram for Continuous Variable
Histogram shows the frequency distribution of a given variable. The below representation groups the frequency bars based on a categorical variable giving a greater insight about the continuous variable and the categorical variable in tandem. Create histogram and learn how to interpret them in this free video tutorial.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare data
x_var = 'displ'
groupby_var = 'class'
df_agg = df.loc[:, [x_var, groupby_var]].groupby(groupby_var)
vals = [df[x_var].values.tolist() for i, df in df_agg]
# Draw
plt.figure(figsize=(16,9), dpi= 80)
colors = [plt.cm.Spectral(i/float(len(vals)-1)) for i in range(len(vals))]
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(vals, 30, stacked=True, density=False, color=colors[:len(vals)])
# Decoration
plt.legend({group:col for group, col in zip(np.unique(df[groupby_var]).tolist(), colors[:len(vals)])})
plt.title(f"Stacked Histogram of ${x_var}$ colored by ${groupby_var}$", fontsize=22)
plt.xlabel(x_var)
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.ylim(0, 25)
plt.xticks(ticks=bins[::3], labels=[round(b,1) for b in bins[::3]])
plt.show()
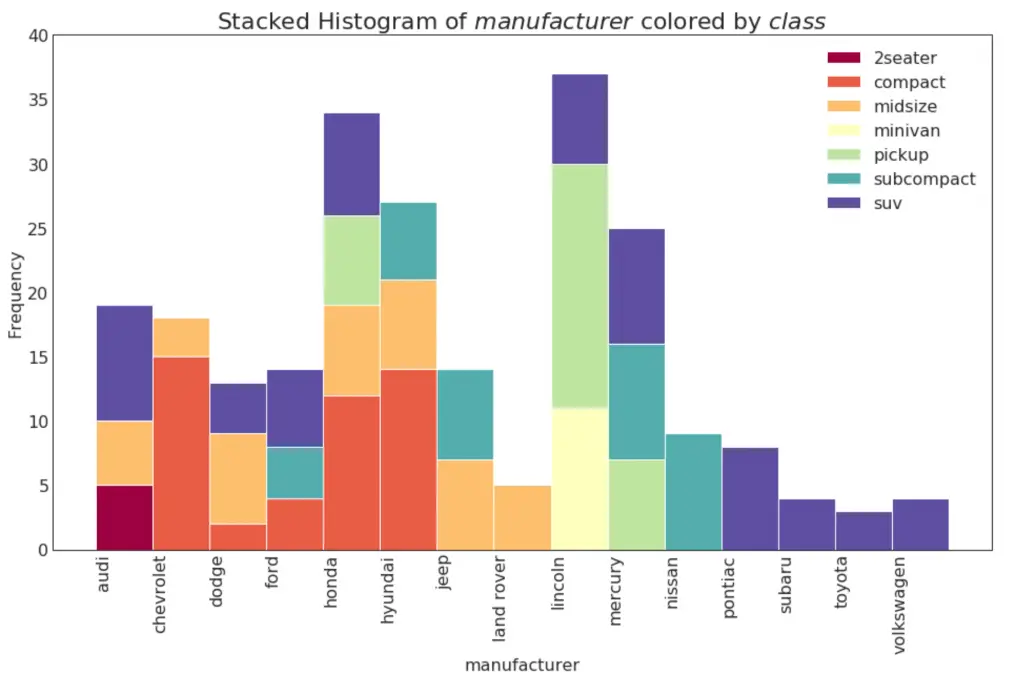
21. Histogram for Categorical Variable
The histogram of a categorical variable shows the frequency distribution of a that variable. By coloring the bars, you can visualize the distribution in connection with another categorical variable representing the colors.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare data
x_var = 'manufacturer'
groupby_var = 'class'
df_agg = df.loc[:, [x_var, groupby_var]].groupby(groupby_var)
vals = [df[x_var].values.tolist() for i, df in df_agg]
# Draw
plt.figure(figsize=(16,9), dpi= 80)
colors = [plt.cm.Spectral(i/float(len(vals)-1)) for i in range(len(vals))]
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(vals, df[x_var].unique().__len__(), stacked=True, density=False, color=colors[:len(vals)])
# Decoration
plt.legend({group:col for group, col in zip(np.unique(df[groupby_var]).tolist(), colors[:len(vals)])})
plt.title(f"Stacked Histogram of ${x_var}$ colored by ${groupby_var}$", fontsize=22)
plt.xlabel(x_var)
plt.ylabel("Frequency")
plt.ylim(0, 40)
plt.xticks(ticks=bins, labels=np.unique(df[x_var]).tolist(), rotation=90, horizontalalignment='left')
plt.show()
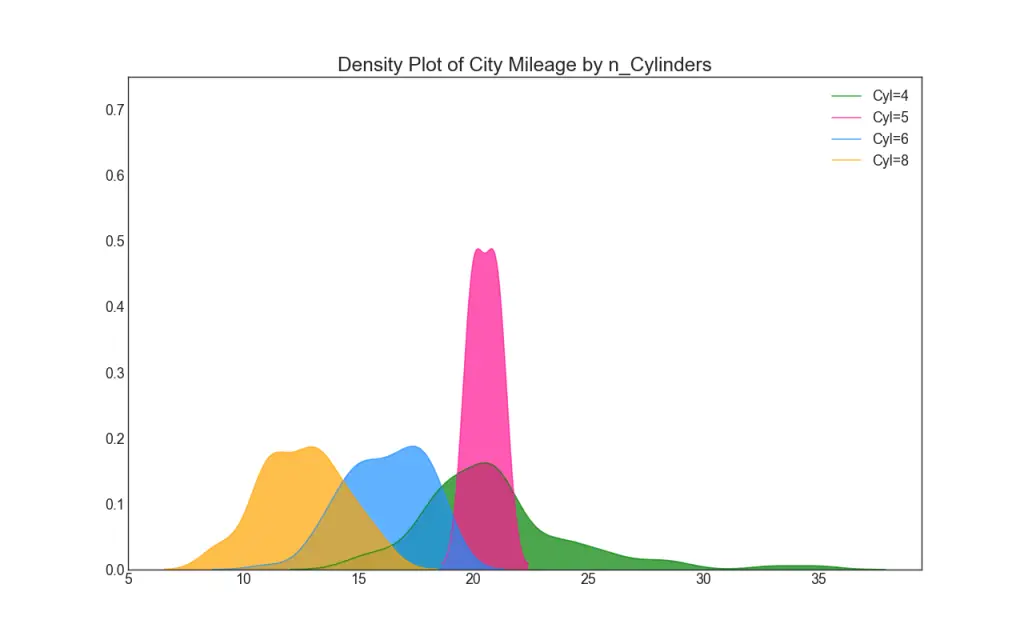
22. Density Plot
Density plots are a commonly used tool visualise the distribution of a continuous variable. By grouping them by the ‘response’ variable, you can inspect the relationship between the X and the Y. The below case if for representational purpose to describe how the distribution of city mileage varies with respect the number of cylinders.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
sns.kdeplot(df.loc[df['cyl'] == 4, "cty"], shade=True, color="g", label="Cyl=4", alpha=.7)
sns.kdeplot(df.loc[df['cyl'] == 5, "cty"], shade=True, color="deeppink", label="Cyl=5", alpha=.7)
sns.kdeplot(df.loc[df['cyl'] == 6, "cty"], shade=True, color="dodgerblue", label="Cyl=6", alpha=.7)
sns.kdeplot(df.loc[df['cyl'] == 8, "cty"], shade=True, color="orange", label="Cyl=8", alpha=.7)
# Decoration
plt.title('Density Plot of City Mileage by n_Cylinders', fontsize=22)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
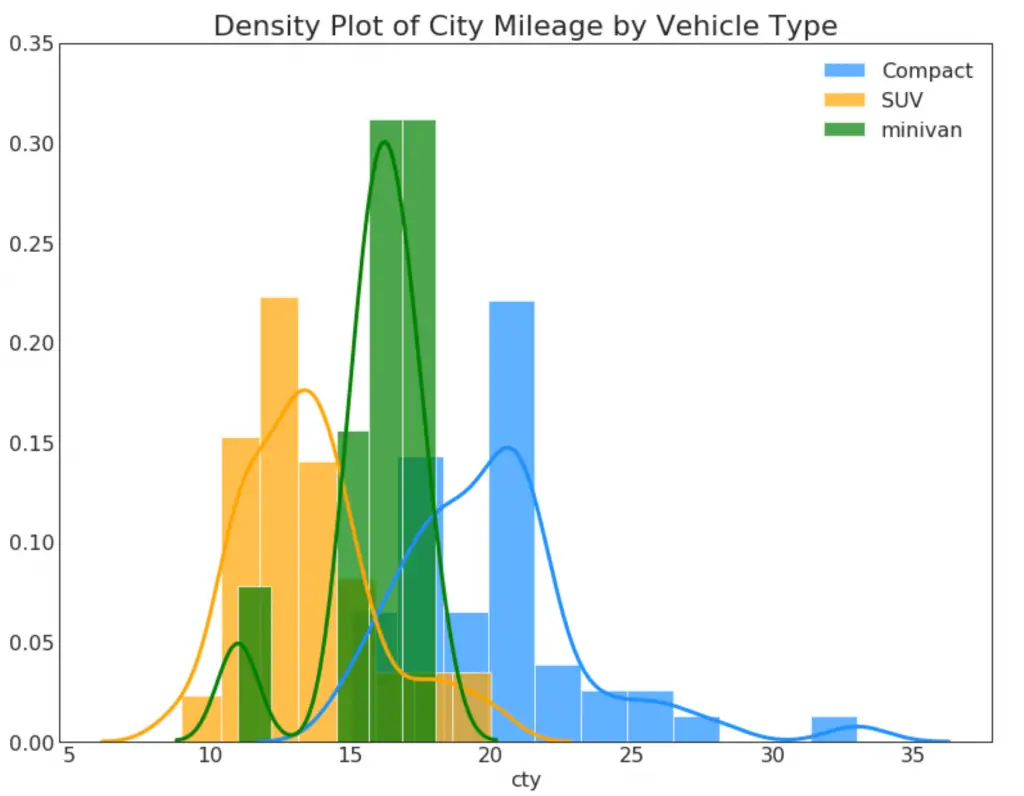
23. Density Curves with Histogram
Density curve with histogram brings together the collective information conveyed by the two plots so you can have them both in a single figure instead of two.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(13,10), dpi= 80)
sns.distplot(df.loc[df['class'] == 'compact', "cty"], color="dodgerblue", label="Compact", hist_kws={'alpha':.7}, kde_kws={'linewidth':3})
sns.distplot(df.loc[df['class'] == 'suv', "cty"], color="orange", label="SUV", hist_kws={'alpha':.7}, kde_kws={'linewidth':3})
sns.distplot(df.loc[df['class'] == 'minivan', "cty"], color="g", label="minivan", hist_kws={'alpha':.7}, kde_kws={'linewidth':3})
plt.ylim(0, 0.35)
# Decoration
plt.title('Density Plot of City Mileage by Vehicle Type', fontsize=22)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
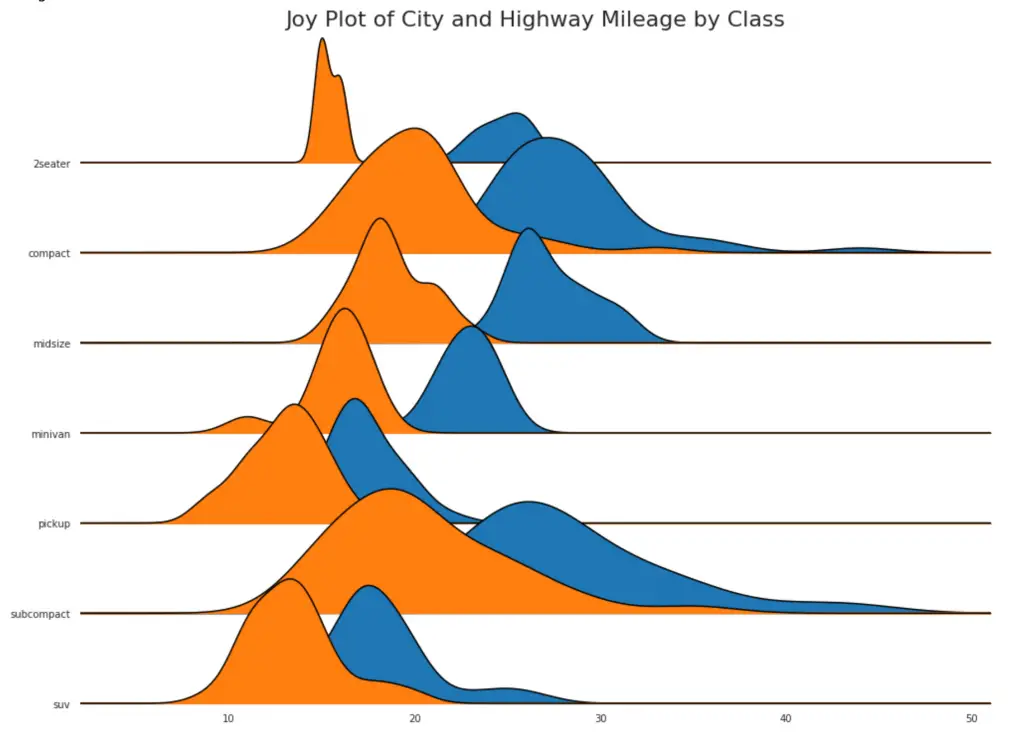
24. Joy Plot
Joy Plot allows the density curves of different groups to overlap, it is a great way to visualize the distribution of a larger number of groups in relation to each other. It looks pleasing to the eye and conveys just the right information clearly. It can be easily built using the joypy package which is based on matplotlib.
# !pip install joypy
# Import Data
mpg = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
fig, axes = joypy.joyplot(mpg, column=['hwy', 'cty'], by="class", ylim='own', figsize=(14,10))
# Decoration
plt.title('Joy Plot of City and Highway Mileage by Class', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
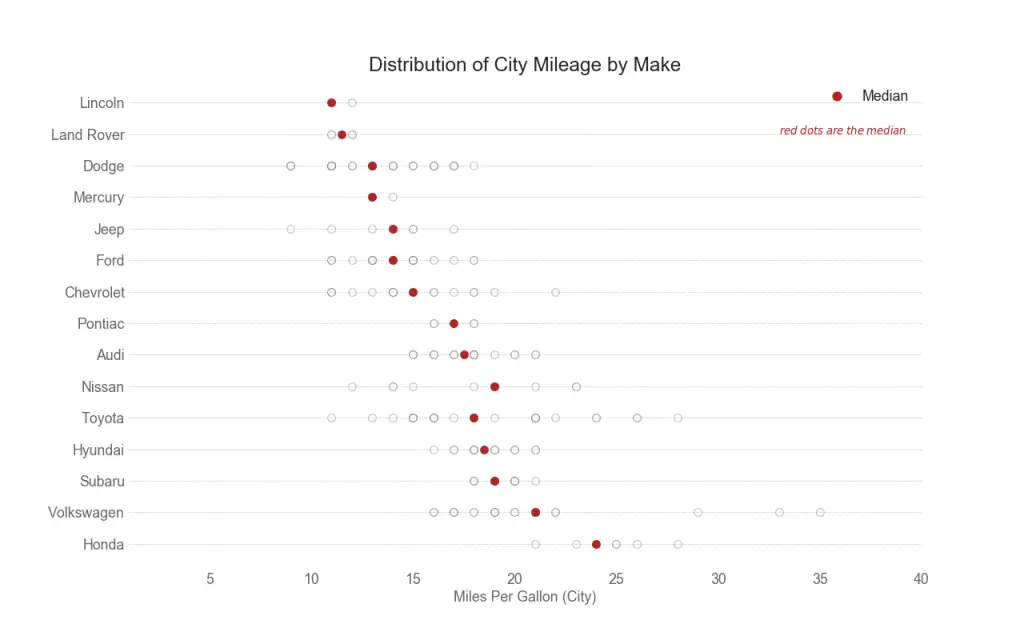
25. Distributed Dot Plot
Distributed dot plot shows the univariate distribution of points segmented by groups. The darker the points, more is the concentration of data points in that region. By coloring the median differently, the real positioning of the groups becomes apparent instantly.
Show Codeimport matplotlib.patches as mpatches
# Prepare Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
cyl_colors = {4:'tab:red', 5:'tab:green', 6:'tab:blue', 8:'tab:orange'}
df_raw['cyl_color'] = df_raw.cyl.map(cyl_colors)
# Mean and Median city mileage by make
df = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.mean())
df.sort_values('cty', ascending=False, inplace=True)
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
df_median = df_raw[['cty', 'manufacturer']].groupby('manufacturer').apply(lambda x: x.median())
# Draw horizontal lines
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
ax.hlines(y=df.index, xmin=0, xmax=40, color='gray', alpha=0.5, linewidth=.5, linestyles='dashdot')
# Draw the Dots
for i, make in enumerate(df.manufacturer):
df_make = df_raw.loc[df_raw.manufacturer==make, :]
ax.scatter(y=np.repeat(i, df_make.shape[0]), x='cty', data=df_make, s=75, edgecolors='gray', c='w', alpha=0.5)
ax.scatter(y=i, x='cty', data=df_median.loc[df_median.index==make, :], s=75, c='firebrick')
# Annotate
ax.text(33, 13, "$red \; dots \; are \; the \: median$", fontdict={'size':12}, color='firebrick')
# Decorations
red_patch = plt.plot([],[], marker="o", ms=10, ls="", mec=None, color='firebrick', label="Median")
plt.legend(handles=red_patch)
ax.set_title('Distribution of City Mileage by Make', fontdict={'size':22})
ax.set_xlabel('Miles Per Gallon (City)', alpha=0.7)
ax.set_yticks(df.index)
ax.set_yticklabels(df.manufacturer.str.title(), fontdict={'horizontalalignment': 'right'}, alpha=0.7)
ax.set_xlim(1, 40)
plt.xticks(alpha=0.7)
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_visible(False)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_visible(False)
plt.grid(axis='both', alpha=.4, linewidth=.1)
plt.show()
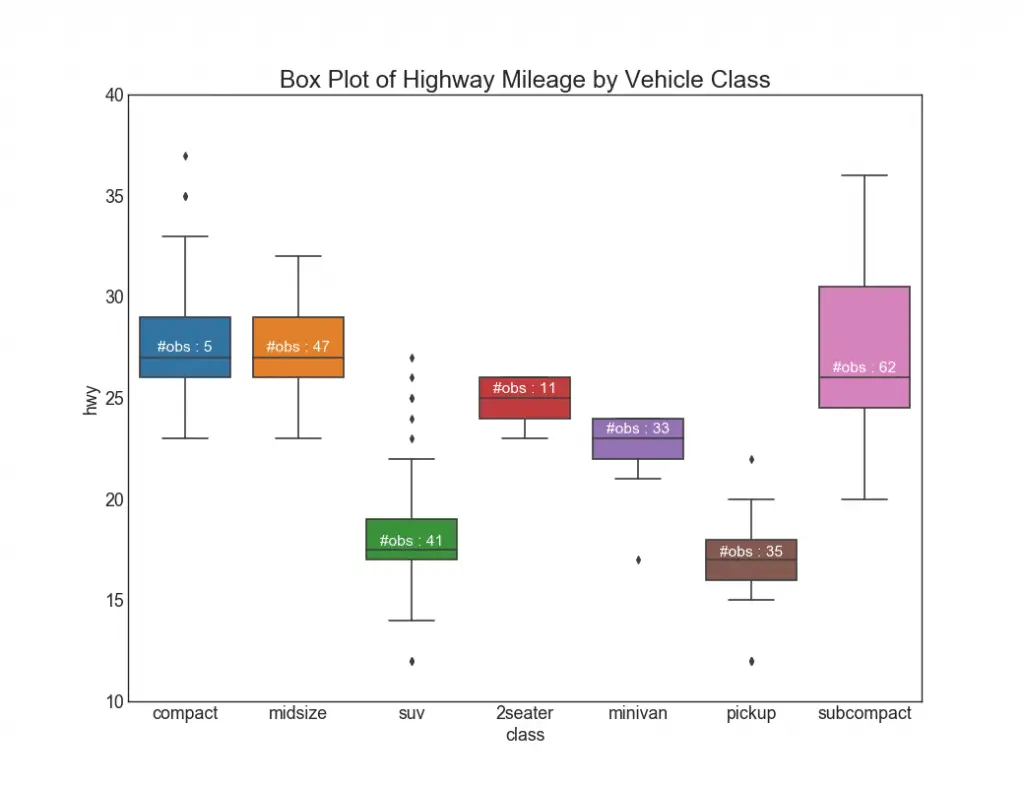
26. Box Plot
Box plots are a great way to visualize the distribution, keeping the median, 25th 75th quartiles and the outliers in mind. However, you need to be careful about interpreting the size the boxes which can potentially distort the number of points contained within that group. So, manually providing the number of observations in each box can help overcome this drawback. Check this free video lesson to visualize distribution of a numeric variable using box plot.
For example, the first two boxes on the left have boxes of the same size even though they have 5 and 47 obs respectively. So writing the number of observations in that group becomes necessary.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(13,10), dpi= 80)
sns.boxplot(x='class', y='hwy', data=df, notch=False)
# Add N Obs inside boxplot (optional)
def add_n_obs(df,group_col,y):
medians_dict = {grp[0]:grp[1][y].median() for grp in df.groupby(group_col)}
xticklabels = [x.get_text() for x in plt.gca().get_xticklabels()]
n_obs = df.groupby(group_col)[y].size().values
for (x, xticklabel), n_ob in zip(enumerate(xticklabels), n_obs):
plt.text(x, medians_dict[xticklabel]*1.01, "#obs : "+str(n_ob), horizontalalignment='center', fontdict={'size':14}, color='white')
add_n_obs(df,group_col='class',y='hwy')
# Decoration
plt.title('Box Plot of Highway Mileage by Vehicle Class', fontsize=22)
plt.ylim(10, 40)
plt.show()
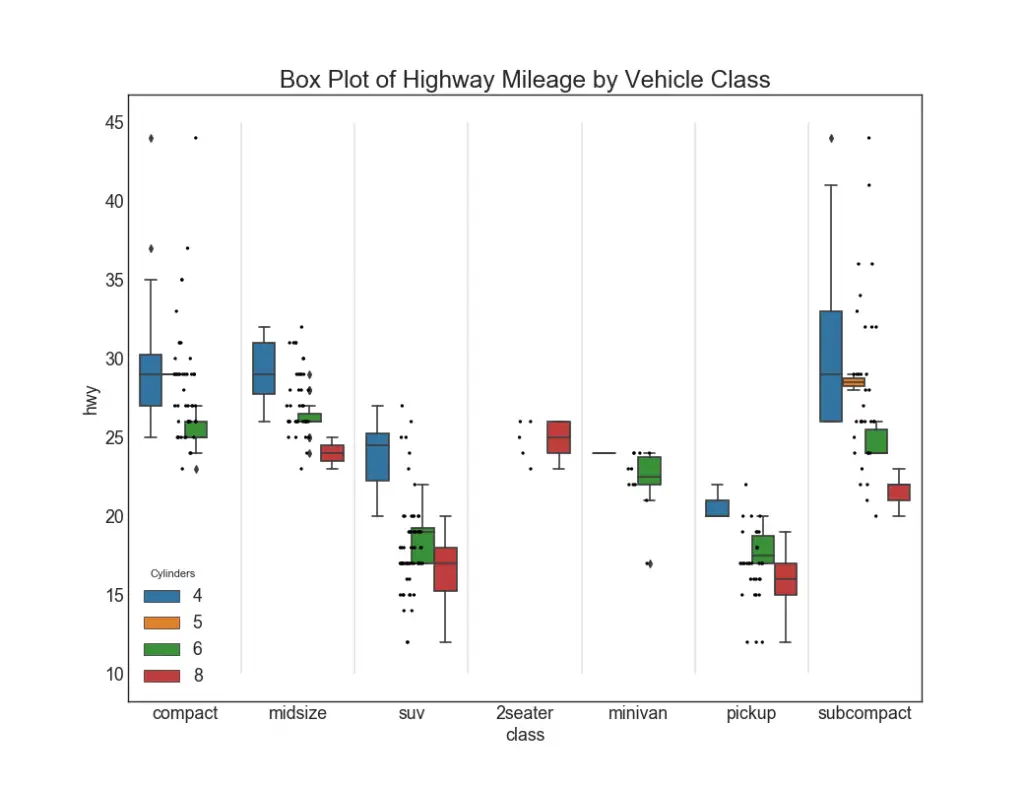
27. Dot + Box Plot
Dot + Box plot Conveys similar information as a boxplot split in groups. The dots, in addition, gives a sense of how many data points lie within each group.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(13,10), dpi= 80)
sns.boxplot(x='class', y='hwy', data=df, hue='cyl')
sns.stripplot(x='class', y='hwy', data=df, color='black', size=3, jitter=1)
for i in range(len(df['class'].unique())-1):
plt.vlines(i+.5, 10, 45, linestyles='solid', colors='gray', alpha=0.2)
# Decoration
plt.title('Box Plot of Highway Mileage by Vehicle Class', fontsize=22)
plt.legend(title='Cylinders')
plt.show()
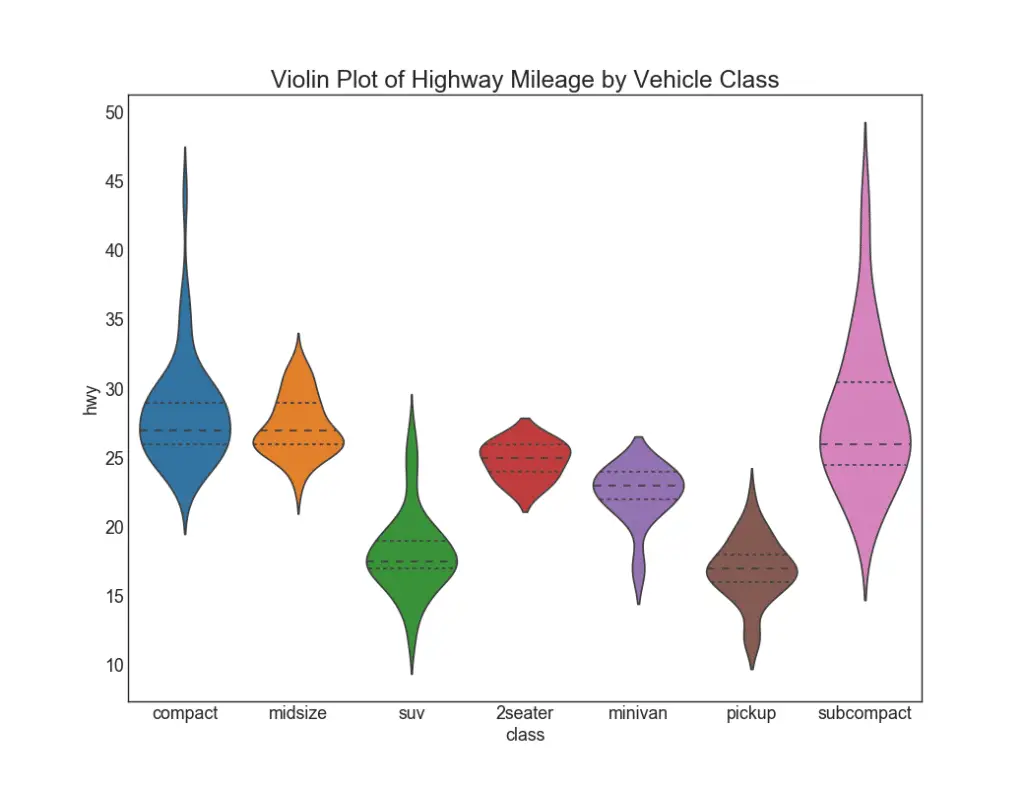
28. Violin Plot
Violin plot is a visually pleasing alternative to box plots. The shape or area of the violin depends on the number of observations it holds. However, the violin plots can be harder to read and it not commonly used in professional settings. Thsi free video tutorial will train you how to implement violin plots.
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(13,10), dpi= 80)
sns.violinplot(x='class', y='hwy', data=df, scale='width', inner='quartile')
# Decoration
plt.title('Violin Plot of Highway Mileage by Vehicle Class', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
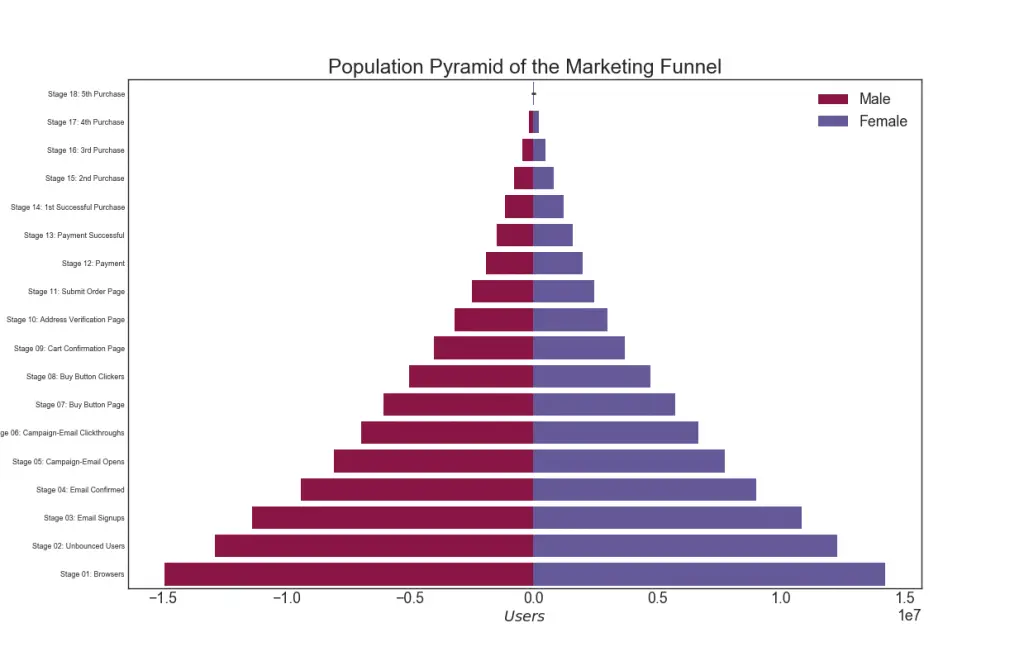
29. Population Pyramid
Population pyramid can be used to show either the distribution of the groups ordered by the volumne. Or it can also be used to show the stage-by-stage filtering of the population as it is used below to show how many people pass through each stage of a marketing funnel.
# Read data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/email_campaign_funnel.csv")
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(13,10), dpi= 80)
group_col = 'Gender'
order_of_bars = df.Stage.unique()[::-1]
colors = [plt.cm.Spectral(i/float(len(df[group_col].unique())-1)) for i in range(len(df[group_col].unique()))]
for c, group in zip(colors, df[group_col].unique()):
sns.barplot(x='Users', y='Stage', data=df.loc[df[group_col]==group, :], order=order_of_bars, color=c, label=group)
# Decorations
plt.xlabel("$Users$")
plt.ylabel("Stage of Purchase")
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.title("Population Pyramid of the Marketing Funnel", fontsize=22)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
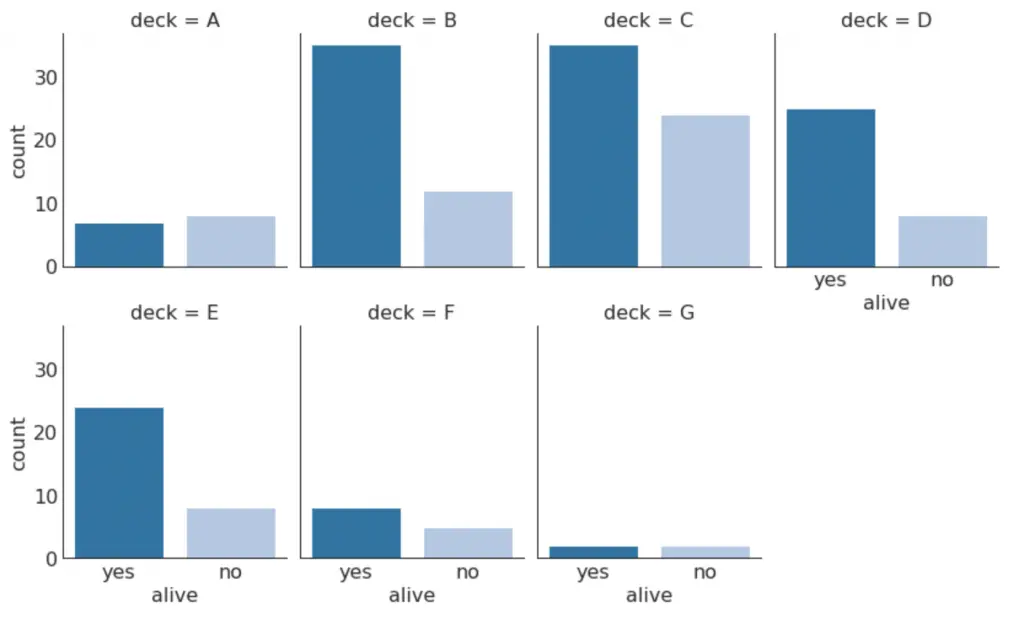
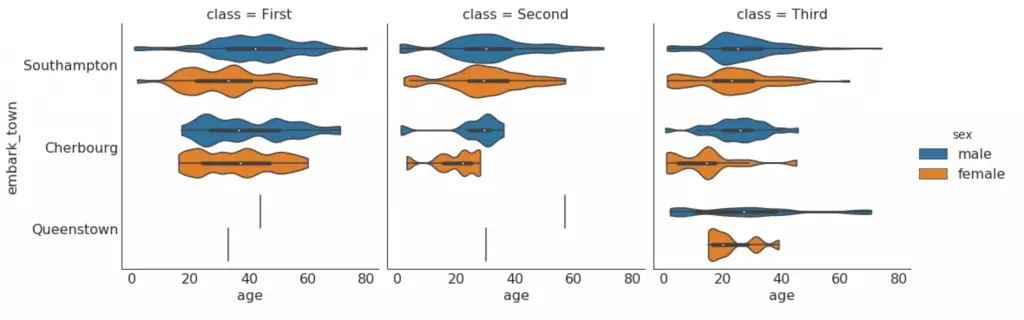
30. Categorical Plots
Categorical plots provided by the seaborn library can be used to visualize the counts distribution of 2 ore more categorical variables in relation to each other.
# Load Dataset
titanic = sns.load_dataset("titanic")
# Plot
g = sns.catplot("alive", col="deck", col_wrap=4,
data=titanic[titanic.deck.notnull()],
kind="count", height=3.5, aspect=.8,
palette='tab20')
fig.suptitle('sf')
plt.show()
# Load Dataset
titanic = sns.load_dataset("titanic")
# Plot
sns.catplot(x="age", y="embark_town",
hue="sex", col="class",
data=titanic[titanic.embark_town.notnull()],
orient="h", height=5, aspect=1, palette="tab10",
kind="violin", dodge=True, cut=0, bw=.2)
Composition
31. Waffle Chart
The waffle chart can be created using the pywaffle package and is used to show the compositions of groups in a larger population.
#! pip install pywaffle
# Reference: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41400136/how-to-do-waffle-charts-in-python-square-piechart
from pywaffle import Waffle
# Import
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare Data
df = df_raw.groupby('class').size().reset_index(name='counts')
n_categories = df.shape[0]
colors = [plt.cm.inferno_r(i/float(n_categories)) for i in range(n_categories)]
# Draw Plot and Decorate
fig = plt.figure(
FigureClass=Waffle,
plots={
'111': {
'values': df['counts'],
'labels': ["{0} ({1})".format(n[0], n[1]) for n in df[['class', 'counts']].itertuples()],
'legend': {'loc': 'upper left', 'bbox_to_anchor': (1.05, 1), 'fontsize': 12},
'title': {'label': '# Vehicles by Class', 'loc': 'center', 'fontsize':18}
},
},
rows=7,
colors=colors,
figsize=(16, 9)
)
#! pip install pywaffle
from pywaffle import Waffle
# Import
# df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare Data
# By Class Data
df_class = df_raw.groupby('class').size().reset_index(name='counts_class')
n_categories = df_class.shape[0]
colors_class = [plt.cm.Set3(i/float(n_categories)) for i in range(n_categories)]
# By Cylinders Data
df_cyl = df_raw.groupby('cyl').size().reset_index(name='counts_cyl')
n_categories = df_cyl.shape[0]
colors_cyl = [plt.cm.Spectral(i/float(n_categories)) for i in range(n_categories)]
# By Make Data
df_make = df_raw.groupby('manufacturer').size().reset_index(name='counts_make')
n_categories = df_make.shape[0]
colors_make = [plt.cm.tab20b(i/float(n_categories)) for i in range(n_categories)]
# Draw Plot and Decorate
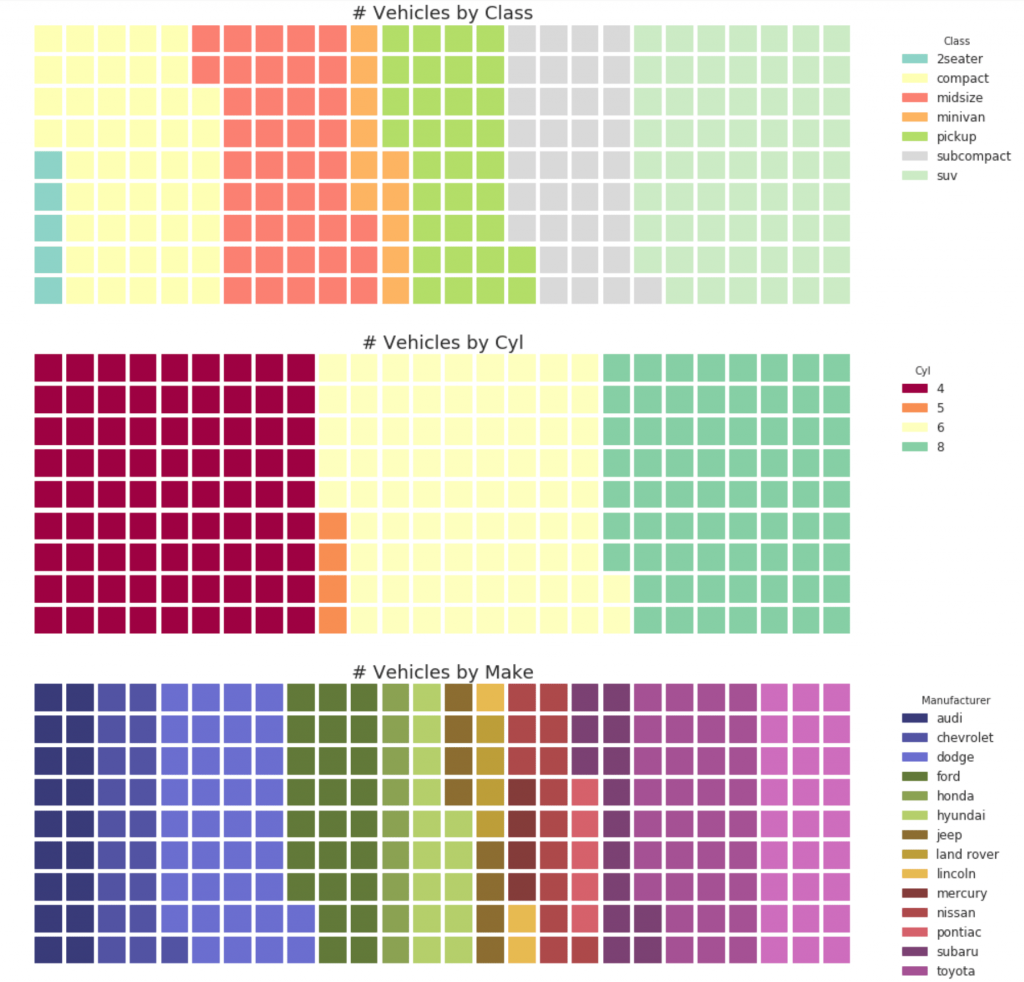
fig = plt.figure(
FigureClass=Waffle,
plots={
'311': {
'values': df_class['counts_class'],
'labels': ["{1}".format(n[0], n[1]) for n in df_class[['class', 'counts_class']].itertuples()],
'legend': {'loc': 'upper left', 'bbox_to_anchor': (1.05, 1), 'fontsize': 12, 'title':'Class'},
'title': {'label': '# Vehicles by Class', 'loc': 'center', 'fontsize':18},
'colors': colors_class
},
'312': {
'values': df_cyl['counts_cyl'],
'labels': ["{1}".format(n[0], n[1]) for n in df_cyl[['cyl', 'counts_cyl']].itertuples()],
'legend': {'loc': 'upper left', 'bbox_to_anchor': (1.05, 1), 'fontsize': 12, 'title':'Cyl'},
'title': {'label': '# Vehicles by Cyl', 'loc': 'center', 'fontsize':18},
'colors': colors_cyl
},
'313': {
'values': df_make['counts_make'],
'labels': ["{1}".format(n[0], n[1]) for n in df_make[['manufacturer', 'counts_make']].itertuples()],
'legend': {'loc': 'upper left', 'bbox_to_anchor': (1.05, 1), 'fontsize': 12, 'title':'Manufacturer'},
'title': {'label': '# Vehicles by Make', 'loc': 'center', 'fontsize':18},
'colors': colors_make
}
},
rows=9,
figsize=(16, 14)
)
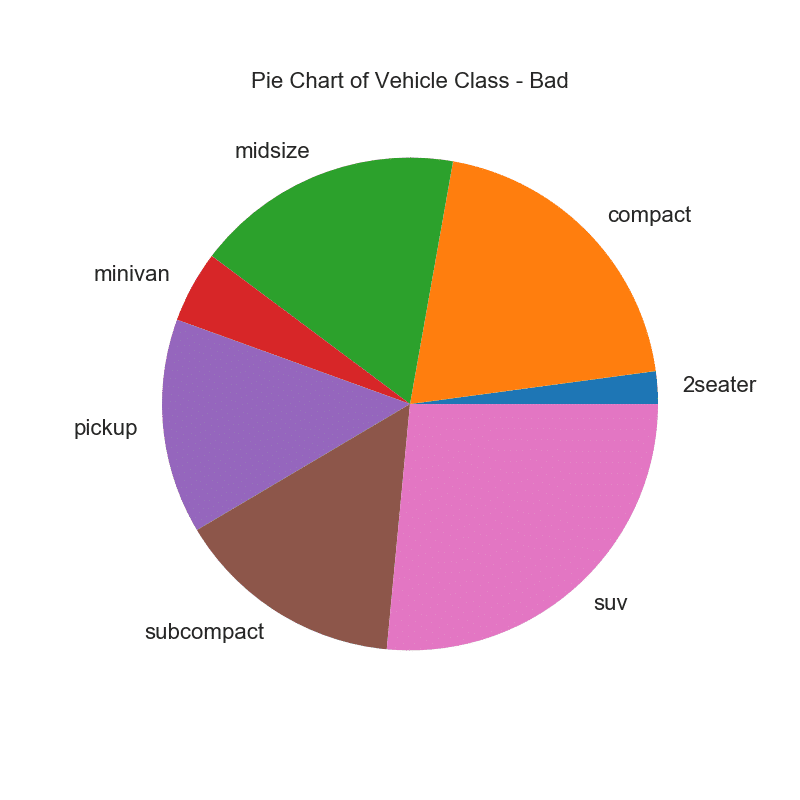
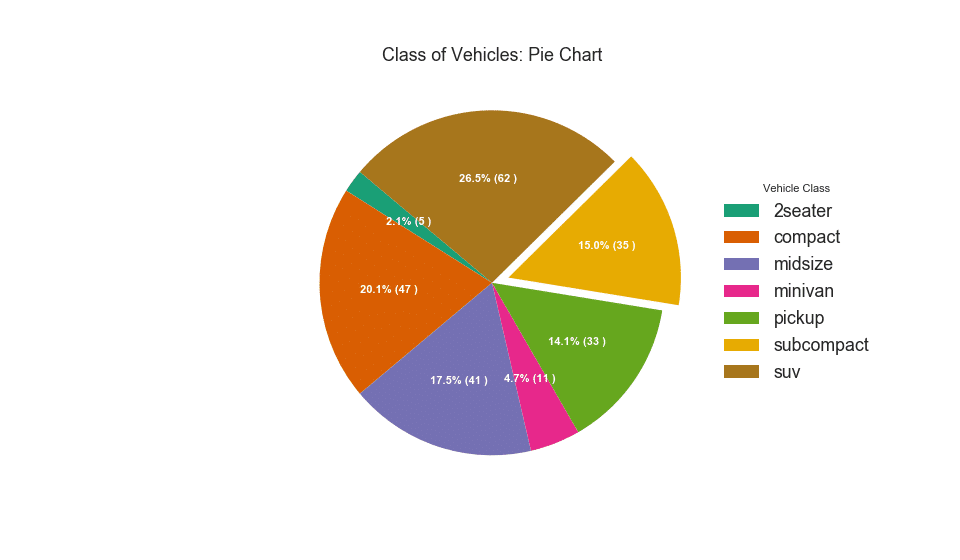
32. Pie Chart
Pie chart is a classic way to show the composition of groups. However, its not generally advisable to use nowadays because the area of the pie portions can sometimes become misleading. So, if you are to use pie chart, its highly recommended to explicitly write down the percentage or numbers for each portion of the pie.
# Import
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare Data
df = df_raw.groupby('class').size()
# Make the plot with pandas
df.plot(kind='pie', subplots=True, figsize=(8, 8), dpi= 80)
plt.title("Pie Chart of Vehicle Class - Bad")
plt.ylabel("")
plt.show()
# Import
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare Data
df = df_raw.groupby('class').size().reset_index(name='counts')
# Draw Plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 7), subplot_kw=dict(aspect="equal"), dpi= 80)
data = df['counts']
categories = df['class']
explode = [0,0,0,0,0,0.1,0]
def func(pct, allvals):
absolute = int(pct/100.*np.sum(allvals))
return "{:.1f}% ({:d} )".format(pct, absolute)
wedges, texts, autotexts = ax.pie(data,
autopct=lambda pct: func(pct, data),
textprops=dict(color="w"),
colors=plt.cm.Dark2.colors,
startangle=140,
explode=explode)
# Decoration
ax.legend(wedges, categories, title="Vehicle Class", loc="center left", bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0, 0.5, 1))
plt.setp(autotexts, size=10, weight=700)
ax.set_title("Class of Vehicles: Pie Chart")
plt.show()
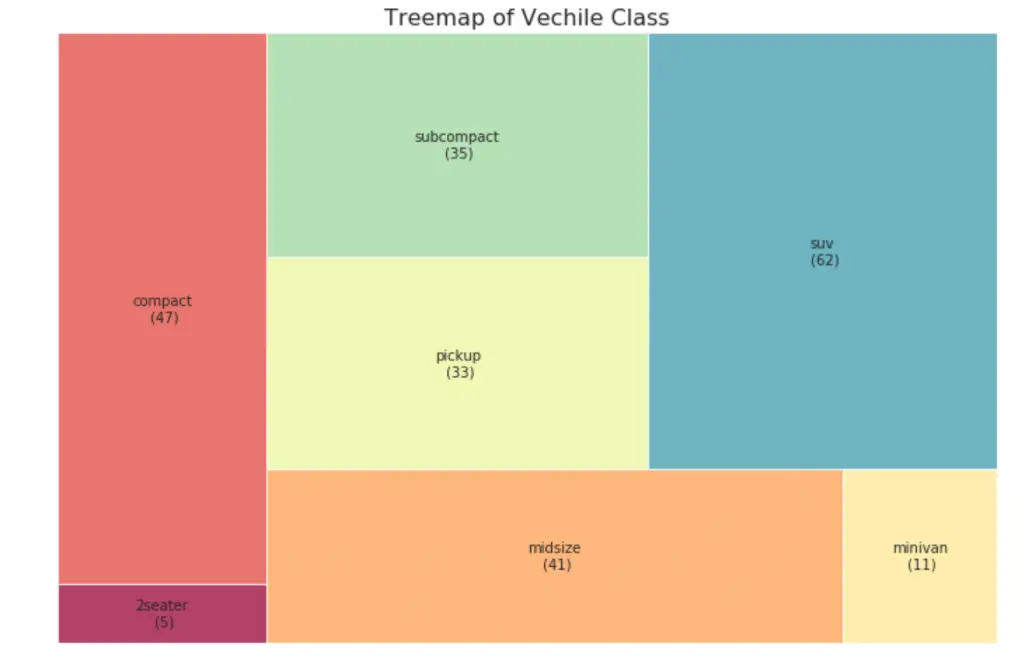
33. Treemap
Tree map is similar to a pie chart and it does a better work without misleading the contributions by each group.
# pip install squarify
import squarify
# Import Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare Data
df = df_raw.groupby('class').size().reset_index(name='counts')
labels = df.apply(lambda x: str(x[0]) + "\n (" + str(x[1]) + ")", axis=1)
sizes = df['counts'].values.tolist()
colors = [plt.cm.Spectral(i/float(len(labels))) for i in range(len(labels))]
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8), dpi= 80)
squarify.plot(sizes=sizes, label=labels, color=colors, alpha=.8)
# Decorate
plt.title('Treemap of Vechile Class')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
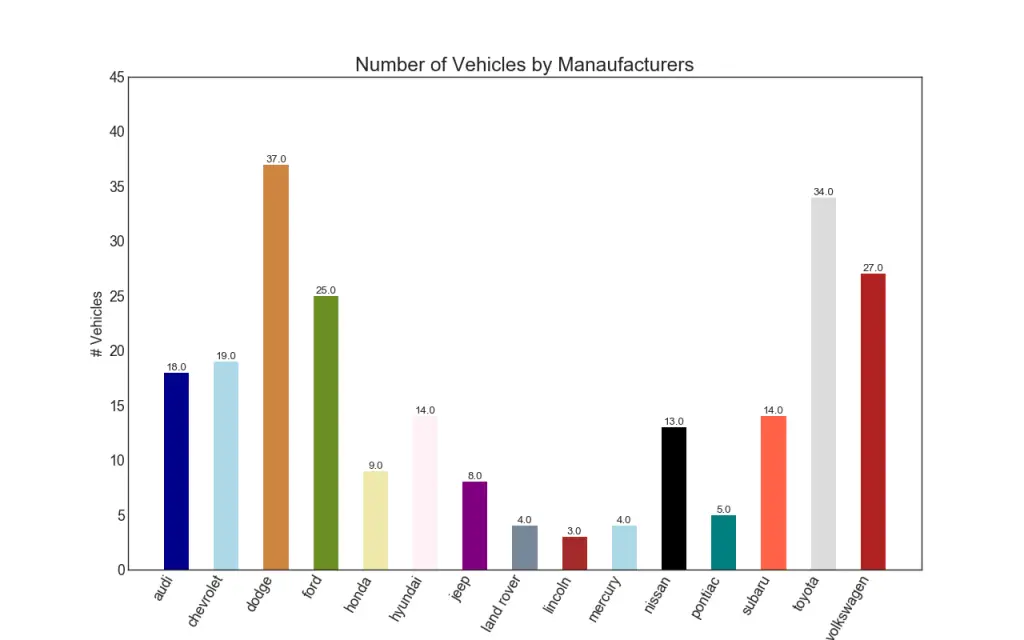
34. Bar Chart
Bar chart is a classic way of visualizing items based on counts or any given metric. In below chart, I have used a different color for each item, but you might typically want to pick one color for all items unless you to color them by groups. The color names get stored inside all_colors in the code below. You can change the color of the bars by setting the color parameter in plt.plot().
import random
# Import Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mpg_ggplot2.csv")
# Prepare Data
df = df_raw.groupby('manufacturer').size().reset_index(name='counts')
n = df['manufacturer'].unique().__len__()+1
all_colors = list(plt.cm.colors.cnames.keys())
random.seed(100)
c = random.choices(all_colors, k=n)
# Plot Bars
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
plt.bar(df['manufacturer'], df['counts'], color=c, width=.5)
for i, val in enumerate(df['counts'].values):
plt.text(i, val, float(val), horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='bottom', fontdict={'fontweight':500, 'size':12})
# Decoration
plt.gca().set_xticklabels(df['manufacturer'], rotation=60, horizontalalignment= 'right')
plt.title("Number of Vehicles by Manaufacturers", fontsize=22)
plt.ylabel('# Vehicles')
plt.ylim(0, 45)
plt.show()
Change
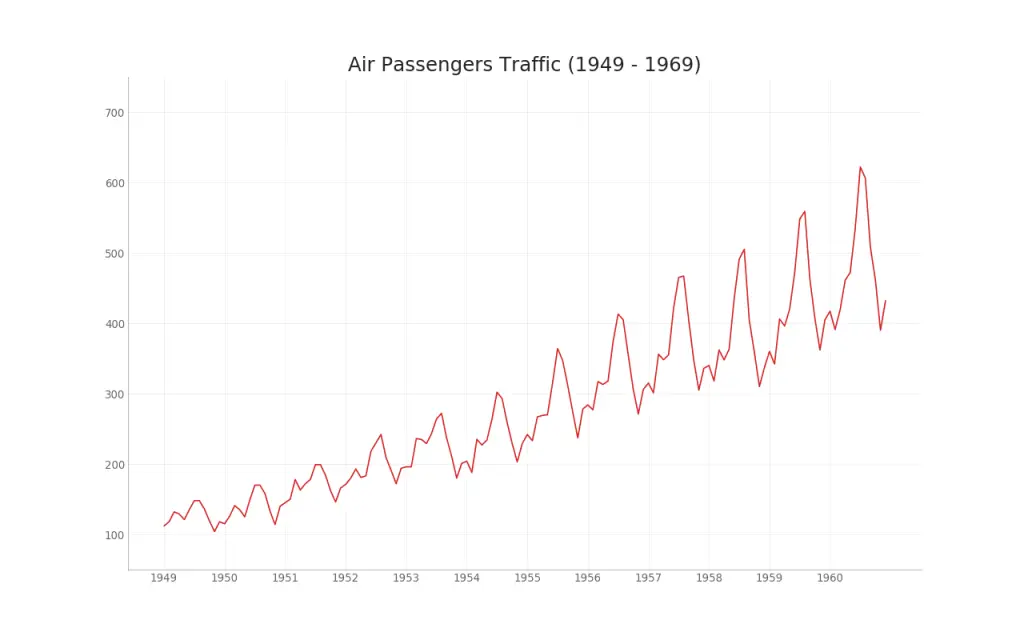
35. Time Series Plot
Time series plot is used to visualise how a given metric changes over time. Here you can see how the Air Passenger traffic changed between 1949 and 1969. Check this free video tutorial on how to implement line plots for analyzing time series.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/AirPassengers.csv')
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
plt.plot('date', 'traffic', data=df, color='tab:red')
# Decoration
plt.ylim(50, 750)
xtick_location = df.index.tolist()[::12]
xtick_labels = [x[-4:] for x in df.date.tolist()[::12]]
plt.xticks(ticks=xtick_location, labels=xtick_labels, rotation=0, fontsize=12, horizontalalignment='center', alpha=.7)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12, alpha=.7)
plt.title("Air Passengers Traffic (1949 - 1969)", fontsize=22)
plt.grid(axis='both', alpha=.3)
# Remove borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(0.0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(0.3)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(0.0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(0.3)
plt.show()
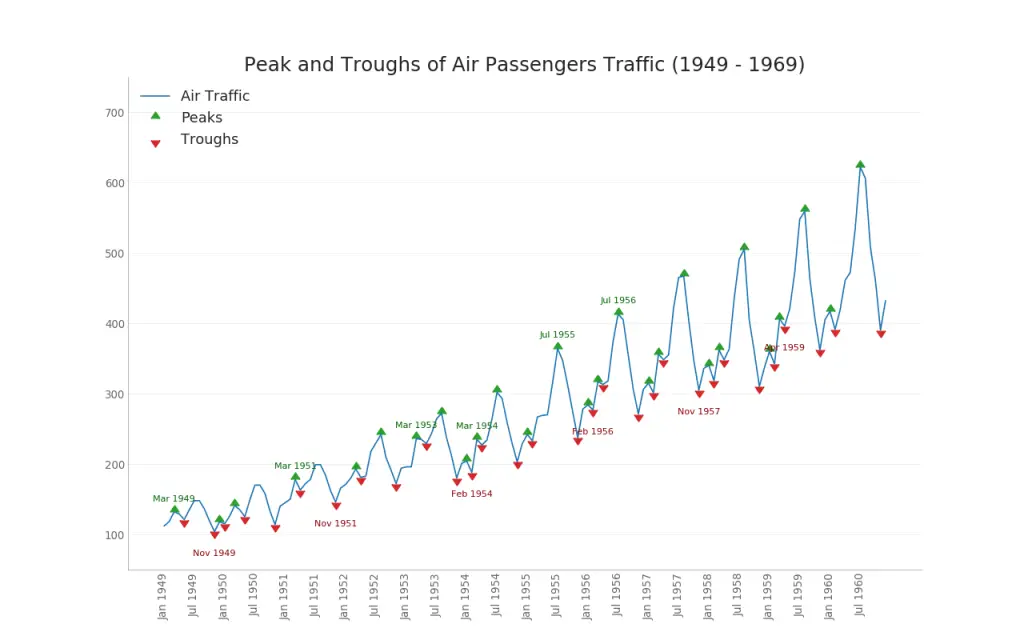
36. Time Series with Peaks and Troughs Annotated
The below time series plots all the the peaks and troughs and annotates the occurence of selected special events.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/AirPassengers.csv')
# Get the Peaks and Troughs
data = df['traffic'].values
doublediff = np.diff(np.sign(np.diff(data)))
peak_locations = np.where(doublediff == -2)[0] + 1
doublediff2 = np.diff(np.sign(np.diff(-1*data)))
trough_locations = np.where(doublediff2 == -2)[0] + 1
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
plt.plot('date', 'traffic', data=df, color='tab:blue', label='Air Traffic')
plt.scatter(df.date[peak_locations], df.traffic[peak_locations], marker=mpl.markers.CARETUPBASE, color='tab:green', s=100, label='Peaks')
plt.scatter(df.date[trough_locations], df.traffic[trough_locations], marker=mpl.markers.CARETDOWNBASE, color='tab:red', s=100, label='Troughs')
# Annotate
for t, p in zip(trough_locations[1::5], peak_locations[::3]):
plt.text(df.date[p], df.traffic[p]+15, df.date[p], horizontalalignment='center', color='darkgreen')
plt.text(df.date[t], df.traffic[t]-35, df.date[t], horizontalalignment='center', color='darkred')
# Decoration
plt.ylim(50,750)
xtick_location = df.index.tolist()[::6]
xtick_labels = df.date.tolist()[::6]
plt.xticks(ticks=xtick_location, labels=xtick_labels, rotation=90, fontsize=12, alpha=.7)
plt.title("Peak and Troughs of Air Passengers Traffic (1949 - 1969)", fontsize=22)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12, alpha=.7)
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(.0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.grid(axis='y', alpha=.3)
plt.show()
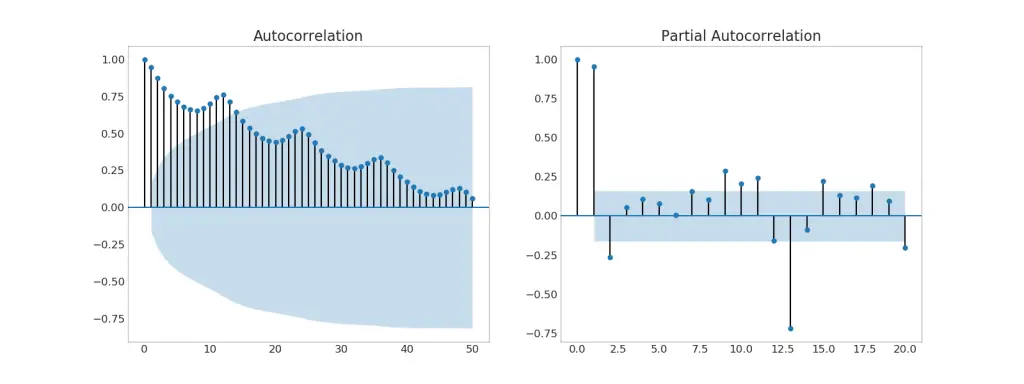
37. Autocorrelation (ACF) and Partial Autocorrelation (PACF) Plot
The ACF plot shows the correlation of the time series with its own lags. Each vertical line (on the autocorrelation plot) represents the correlation between the series and its lag starting from lag 0. The blue shaded region in the plot is the significance level. Those lags that lie above the blue line are the significant lags.
So how to interpret this?
For AirPassengers, we see upto 14 lags have crossed the blue line and so are significant. This means, the Air Passengers traffic seen upto 14 years back has an influence on the traffic seen today.
PACF on the other had shows the autocorrelation of any given lag (of time series) against the current series, but with the contributions of the lags-inbetween removed.
Note: If you want to learn how to interpret and draw ACF and PACF plots, check this free video tutorial.
from statsmodels.graphics.tsaplots import plot_acf, plot_pacf
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/AirPassengers.csv')
# Draw Plot
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2,figsize=(16,6), dpi= 80)
plot_acf(df.traffic.tolist(), ax=ax1, lags=50)
plot_pacf(df.traffic.tolist(), ax=ax2, lags=20)
# Decorate
# lighten the borders
ax1.spines["top"].set_alpha(.3); ax2.spines["top"].set_alpha(.3)
ax1.spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3); ax2.spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3)
ax1.spines["right"].set_alpha(.3); ax2.spines["right"].set_alpha(.3)
ax1.spines["left"].set_alpha(.3); ax2.spines["left"].set_alpha(.3)
# font size of tick labels
ax1.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=12)
ax2.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=12)
plt.show()
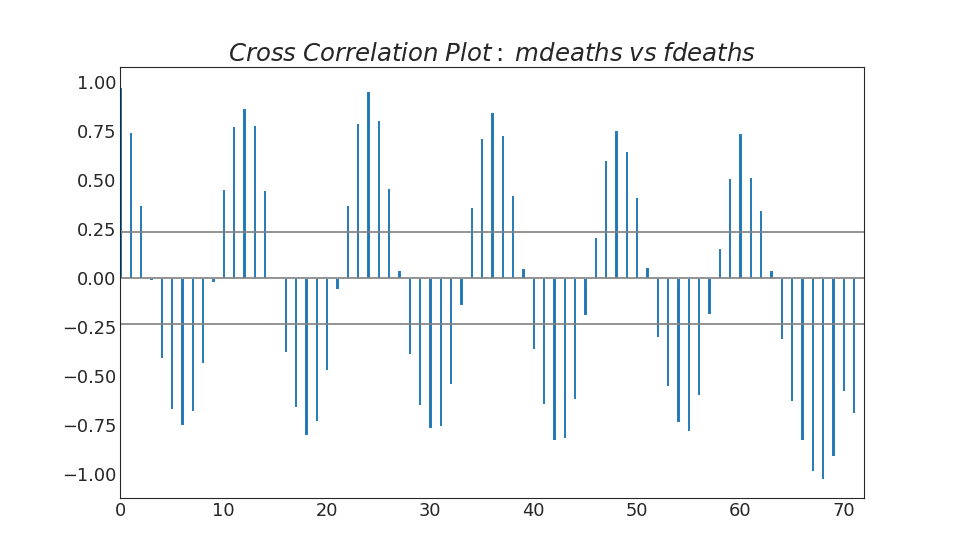
38. Cross Correlation plot
Cross correlation plot shows the lags of two time series with each other.
Show Codeimport statsmodels.tsa.stattools as stattools
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mortality.csv')
x = df['mdeaths']
y = df['fdeaths']
# Compute Cross Correlations
ccs = stattools.ccf(x, y)[:100]
nlags = len(ccs)
# Compute the Significance level
# ref: https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/3115/cross-correlation-significance-in-r/3128#3128
conf_level = 2 / np.sqrt(nlags)
# Draw Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(12,7), dpi= 80)
plt.hlines(0, xmin=0, xmax=100, color='gray') # 0 axis
plt.hlines(conf_level, xmin=0, xmax=100, color='gray')
plt.hlines(-conf_level, xmin=0, xmax=100, color='gray')
plt.bar(x=np.arange(len(ccs)), height=ccs, width=.3)
# Decoration
plt.title('$Cross\; Correlation\; Plot:\; mdeaths\; vs\; fdeaths$', fontsize=22)
plt.xlim(0,len(ccs))
plt.show()
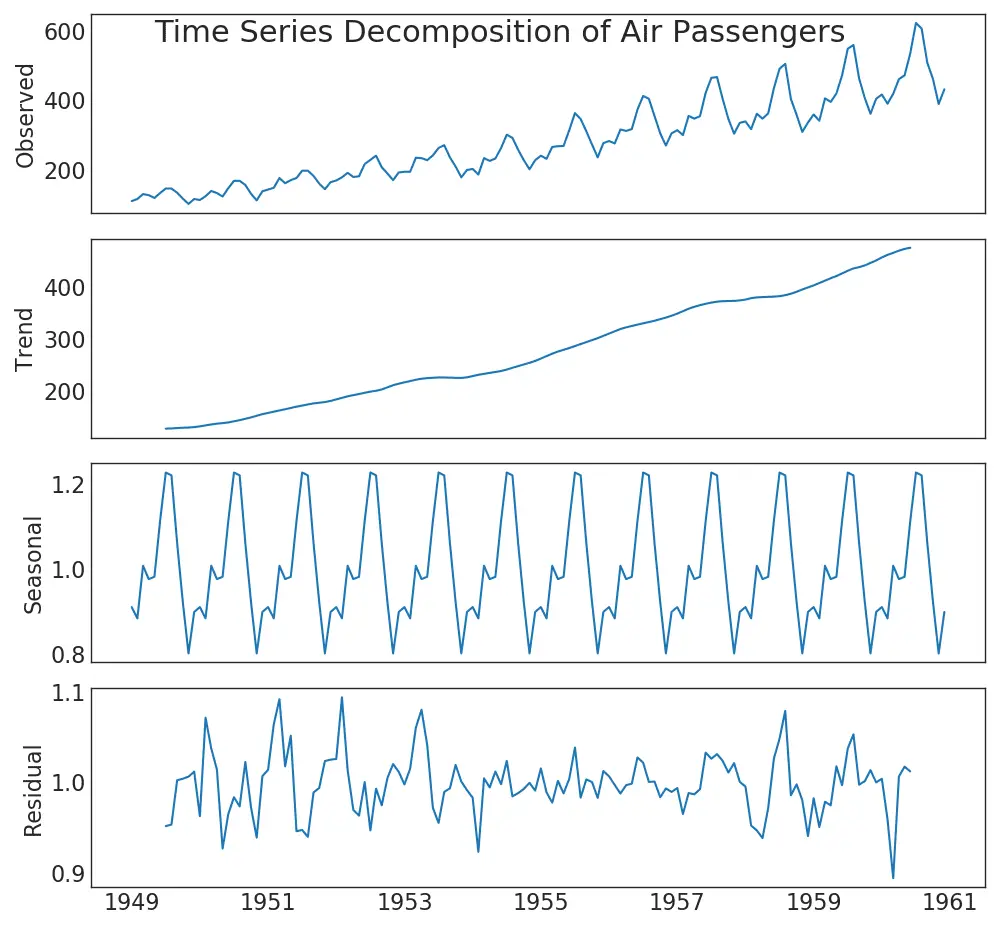
39. Time Series Decomposition Plot
Time series decomposition plot shows the break down of the time series into trend, seasonal and residual components.
from statsmodels.tsa.seasonal import seasonal_decompose
from dateutil.parser import parse
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/AirPassengers.csv')
dates = pd.DatetimeIndex([parse(d).strftime('%Y-%m-01') for d in df['date']])
df.set_index(dates, inplace=True)
# Decompose
result = seasonal_decompose(df['traffic'], model='multiplicative')
# Plot
plt.rcParams.update({'figure.figsize': (10,10)})
result.plot().suptitle('Time Series Decomposition of Air Passengers')
plt.show()
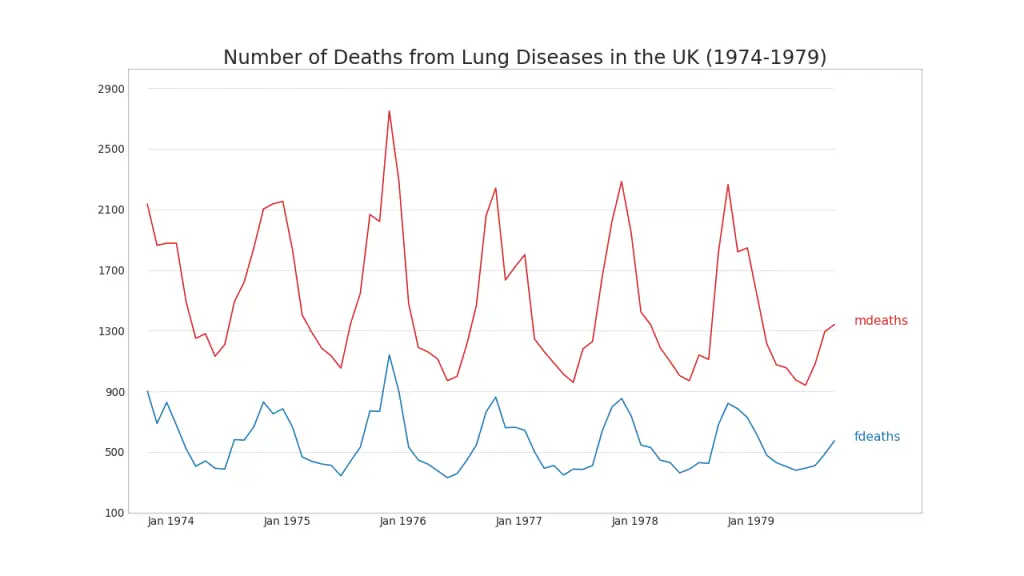
40. Multiple Time Series
You can plot multiple time series that measures the same value on the same chart as shown below.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mortality.csv')
# Define the upper limit, lower limit, interval of Y axis and colors
y_LL = 100
y_UL = int(df.iloc[:, 1:].max().max()*1.1)
y_interval = 400
mycolors = ['tab:red', 'tab:blue', 'tab:green', 'tab:orange']
# Draw Plot and Annotate
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(16, 9), dpi= 80)
columns = df.columns[1:]
for i, column in enumerate(columns):
plt.plot(df.date.values, df[column].values, lw=1.5, color=mycolors[i])
plt.text(df.shape[0]+1, df[column].values[-1], column, fontsize=14, color=mycolors[i])
# Draw Tick lines
for y in range(y_LL, y_UL, y_interval):
plt.hlines(y, xmin=0, xmax=71, colors='black', alpha=0.3, linestyles="--", lw=0.5)
# Decorations
plt.tick_params(axis="both", which="both", bottom=False, top=False,
labelbottom=True, left=False, right=False, labelleft=True)
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.title('Number of Deaths from Lung Diseases in the UK (1974-1979)', fontsize=22)
plt.yticks(range(y_LL, y_UL, y_interval), [str(y) for y in range(y_LL, y_UL, y_interval)], fontsize=12)
plt.xticks(range(0, df.shape[0], 12), df.date.values[::12], horizontalalignment='left', fontsize=12)
plt.ylim(y_LL, y_UL)
plt.xlim(-2, 80)
plt.show()
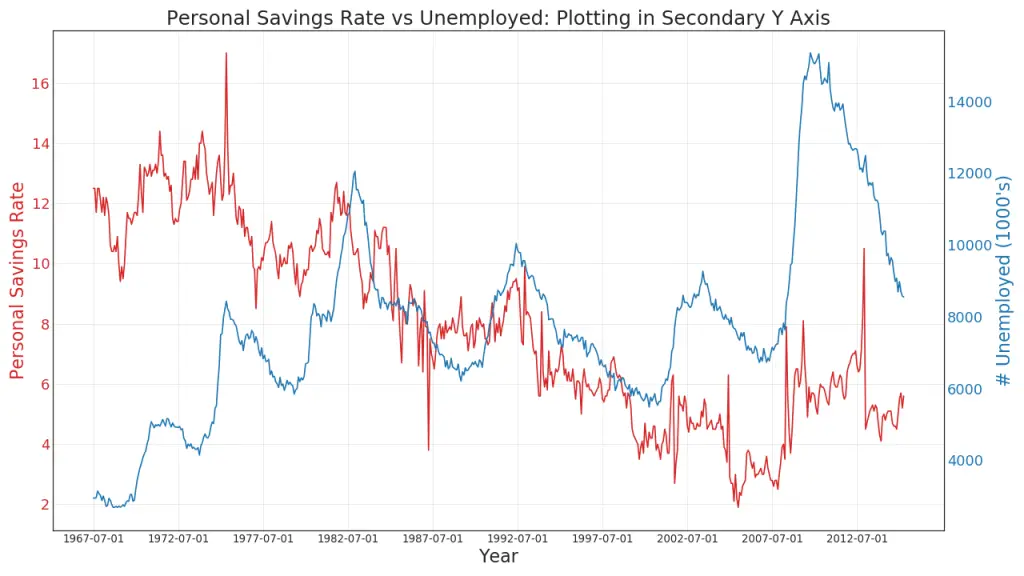
41. Plotting with different scales using secondary Y axis
If you want to show two time series that measures two different quantities at the same point in time, you can plot the second series againt the secondary Y axis on the right.
Learn to draw a multiple axis time series using this free video tutorial.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/economics.csv")
x = df['date']
y1 = df['psavert']
y2 = df['unemploy']
# Plot Line1 (Left Y Axis)
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(16,9), dpi= 80)
ax1.plot(x, y1, color='tab:red')
# Plot Line2 (Right Y Axis)
ax2 = ax1.twinx() # instantiate a second axes that shares the same x-axis
ax2.plot(x, y2, color='tab:blue')
# Decorations
# ax1 (left Y axis)
ax1.set_xlabel('Year', fontsize=20)
ax1.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=0, labelsize=12)
ax1.set_ylabel('Personal Savings Rate', color='tab:red', fontsize=20)
ax1.tick_params(axis='y', rotation=0, labelcolor='tab:red' )
ax1.grid(alpha=.4)
# ax2 (right Y axis)
ax2.set_ylabel("# Unemployed (1000's)", color='tab:blue', fontsize=20)
ax2.tick_params(axis='y', labelcolor='tab:blue')
ax2.set_xticks(np.arange(0, len(x), 60))
ax2.set_xticklabels(x[::60], rotation=90, fontdict={'fontsize':10})
ax2.set_title("Personal Savings Rate vs Unemployed: Plotting in Secondary Y Axis", fontsize=22)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
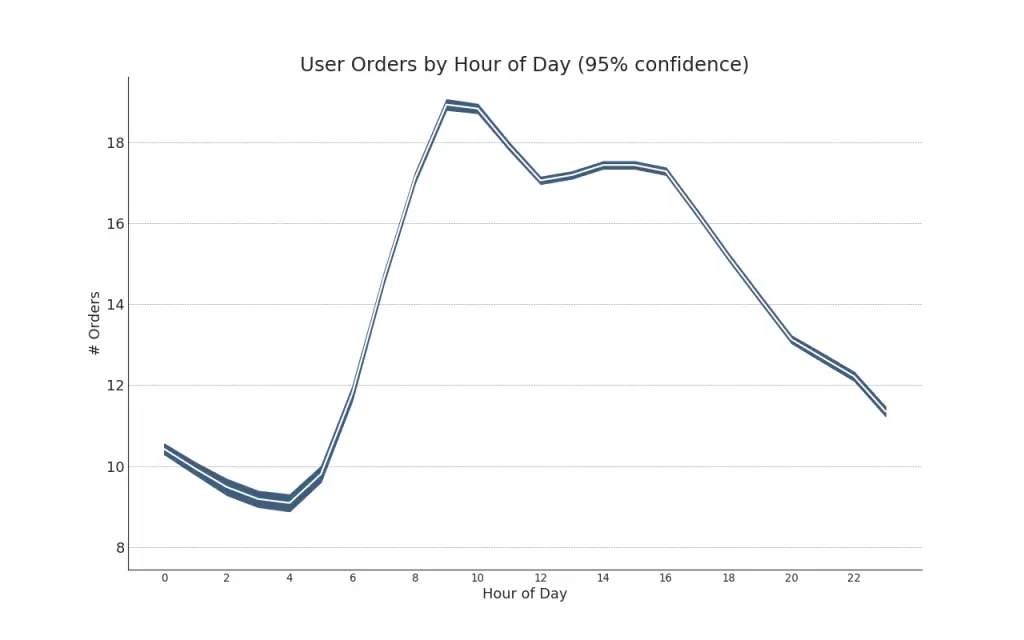
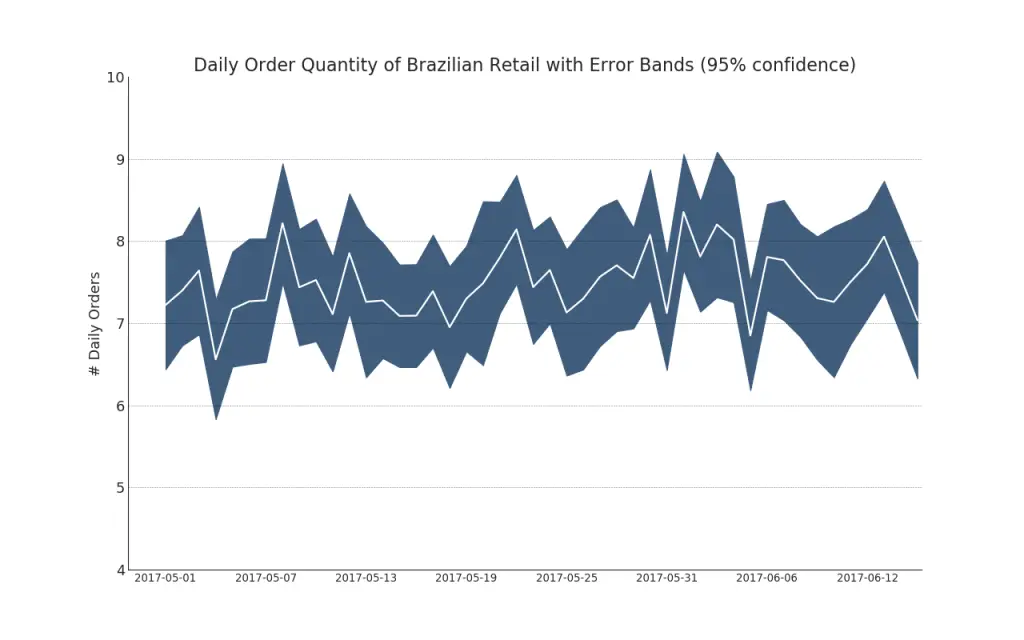
42. Time Series with Error Bands
Time series with error bands can be constructed if you have a time series dataset with multiple observations for each time point (date / timestamp). Below you can see a couple of examples based on the orders coming in at various times of the day. And another example on the number of orders arriving over a duration of 45 days.
In this approach, the mean of the number of orders is denoted by the white line. And a 95% confidence bands are computed and drawn around the mean.
Show Codefrom scipy.stats import sem
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/user_orders_hourofday.csv")
df_mean = df.groupby('order_hour_of_day').quantity.mean()
df_se = df.groupby('order_hour_of_day').quantity.apply(sem).mul(1.96)
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
plt.ylabel("# Orders", fontsize=16)
x = df_mean.index
plt.plot(x, df_mean, color="white", lw=2)
plt.fill_between(x, df_mean - df_se, df_mean + df_se, color="#3F5D7D")
# Decorations
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(1)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(1)
plt.xticks(x[::2], [str(d) for d in x[::2]] , fontsize=12)
plt.title("User Orders by Hour of Day (95% confidence)", fontsize=22)
plt.xlabel("Hour of Day")
s, e = plt.gca().get_xlim()
plt.xlim(s, e)
# Draw Horizontal Tick lines
for y in range(8, 20, 2):
plt.hlines(y, xmin=s, xmax=e, colors='black', alpha=0.5, linestyles="--", lw=0.5)
plt.show()
"Data Source: https://www.kaggle.com/olistbr/brazilian-ecommerce#olist_orders_dataset.csv"
from dateutil.parser import parse
from scipy.stats import sem
# Import Data
df_raw = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/orders_45d.csv',
parse_dates=['purchase_time', 'purchase_date'])
# Prepare Data: Daily Mean and SE Bands
df_mean = df_raw.groupby('purchase_date').quantity.mean()
df_se = df_raw.groupby('purchase_date').quantity.apply(sem).mul(1.96)
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
plt.ylabel("# Daily Orders", fontsize=16)
x = [d.date().strftime('%Y-%m-%d') for d in df_mean.index]
plt.plot(x, df_mean, color="white", lw=2)
plt.fill_between(x, df_mean - df_se, df_mean + df_se, color="#3F5D7D")
# Decorations
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(1)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(1)
plt.xticks(x[::6], [str(d) for d in x[::6]] , fontsize=12)
plt.title("Daily Order Quantity of Brazilian Retail with Error Bands (95% confidence)", fontsize=20)
# Axis limits
s, e = plt.gca().get_xlim()
plt.xlim(s, e-2)
plt.ylim(4, 10)
# Draw Horizontal Tick lines
for y in range(5, 10, 1):
plt.hlines(y, xmin=s, xmax=e, colors='black', alpha=0.5, linestyles="--", lw=0.5)
plt.show()
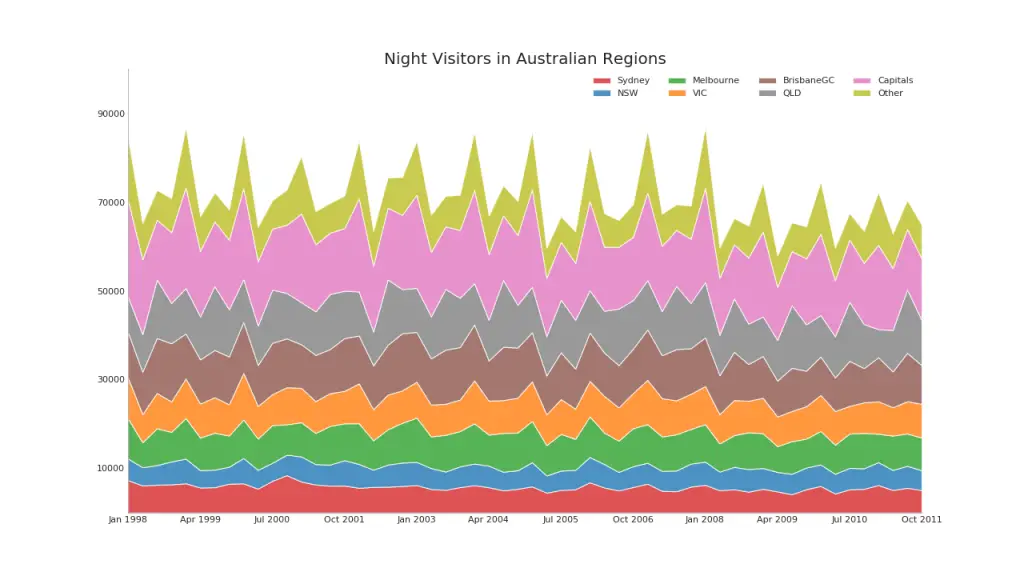
43. Stacked Area Chart
Stacked area chart gives an visual representation of the extent of contribution from multiple time series so that it is easy to compare against each other.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/nightvisitors.csv')
# Decide Colors
mycolors = ['tab:red', 'tab:blue', 'tab:green', 'tab:orange', 'tab:brown', 'tab:grey', 'tab:pink', 'tab:olive']
# Draw Plot and Annotate
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(16, 9), dpi= 80)
columns = df.columns[1:]
labs = columns.values.tolist()
# Prepare data
x = df['yearmon'].values.tolist()
y0 = df[columns[0]].values.tolist()
y1 = df[columns[1]].values.tolist()
y2 = df[columns[2]].values.tolist()
y3 = df[columns[3]].values.tolist()
y4 = df[columns[4]].values.tolist()
y5 = df[columns[5]].values.tolist()
y6 = df[columns[6]].values.tolist()
y7 = df[columns[7]].values.tolist()
y = np.vstack([y0, y2, y4, y6, y7, y5, y1, y3])
# Plot for each column
labs = columns.values.tolist()
ax = plt.gca()
ax.stackplot(x, y, labels=labs, colors=mycolors, alpha=0.8)
# Decorations
ax.set_title('Night Visitors in Australian Regions', fontsize=18)
ax.set(ylim=[0, 100000])
ax.legend(fontsize=10, ncol=4)
plt.xticks(x[::5], fontsize=10, horizontalalignment='center')
plt.yticks(np.arange(10000, 100000, 20000), fontsize=10)
plt.xlim(x[0], x[-1])
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.show()
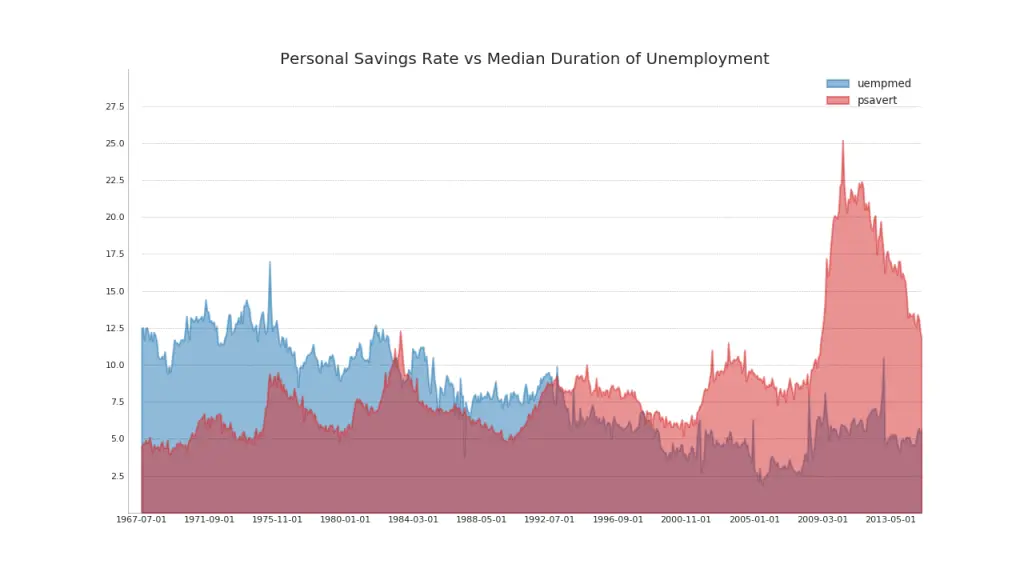
44. Area Chart UnStacked
An unstacked area chart is used to visualize the progress (ups and downs) of two or more series with respect to each other. In the chart below, you can clearly see how the personal savings rate comes down as the median duration of unemployment increases. The unstacked area chart brings out this phenomenon nicely.
Show Code# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/economics.csv")
# Prepare Data
x = df['date'].values.tolist()
y1 = df['psavert'].values.tolist()
y2 = df['uempmed'].values.tolist()
mycolors = ['tab:red', 'tab:blue', 'tab:green', 'tab:orange', 'tab:brown', 'tab:grey', 'tab:pink', 'tab:olive']
columns = ['psavert', 'uempmed']
# Draw Plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(16,9), dpi= 80)
ax.fill_between(x, y1=y1, y2=0, label=columns[1], alpha=0.5, color=mycolors[1], linewidth=2)
ax.fill_between(x, y1=y2, y2=0, label=columns[0], alpha=0.5, color=mycolors[0], linewidth=2)
# Decorations
ax.set_title('Personal Savings Rate vs Median Duration of Unemployment', fontsize=18)
ax.set(ylim=[0, 30])
ax.legend(loc='best', fontsize=12)
plt.xticks(x[::50], fontsize=10, horizontalalignment='center')
plt.yticks(np.arange(2.5, 30.0, 2.5), fontsize=10)
plt.xlim(-10, x[-1])
# Draw Tick lines
for y in np.arange(2.5, 30.0, 2.5):
plt.hlines(y, xmin=0, xmax=len(x), colors='black', alpha=0.3, linestyles="--", lw=0.5)
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.show()
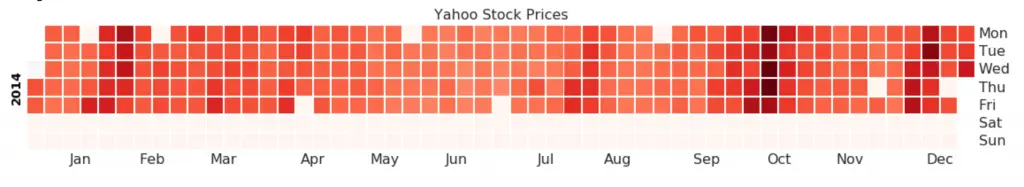
45. Calendar Heat Map
Calendar map is an alternate and a less preferred option to visualise time based data compared to a time series. Though can be visually appealing, the numeric values are not quite evident. It is however effective in picturising the extreme values and holiday effects nicely.
import matplotlib as mpl
import calmap
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/yahoo.csv", parse_dates=['date'])
df.set_index('date', inplace=True)
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
calmap.calendarplot(df['2014']['VIX.Close'], fig_kws={'figsize': (16,10)}, yearlabel_kws={'color':'black', 'fontsize':14}, subplot_kws={'title':'Yahoo Stock Prices'})
plt.show()
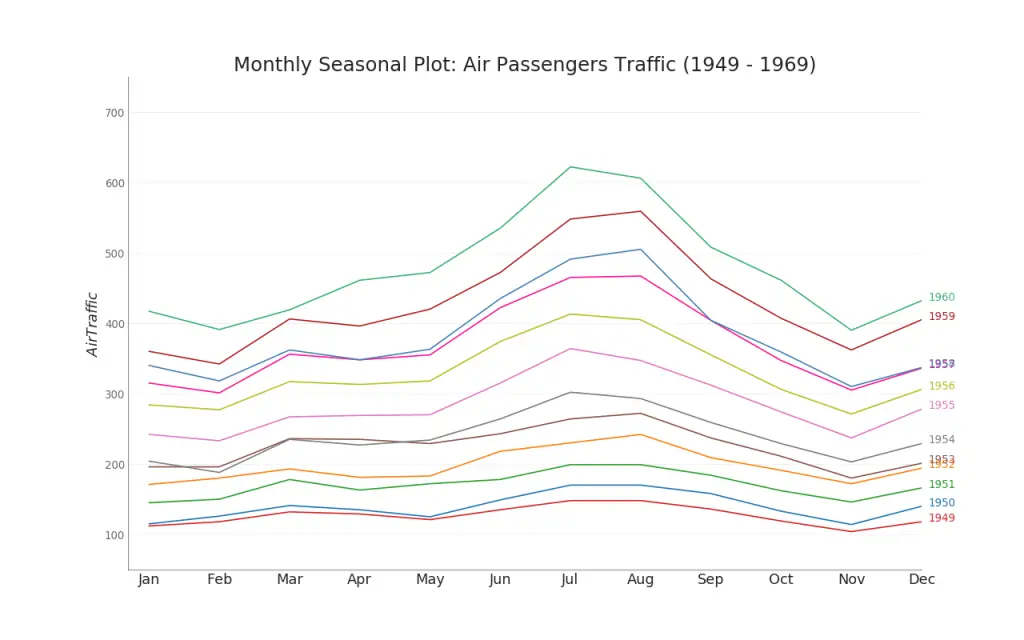
46. Seasonal Plot
The seasonal plot can be used to compare how the time series performed at same day in the previous season (year / month / week etc).
Show Codefrom dateutil.parser import parse
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/AirPassengers.csv')
# Prepare data
df['year'] = [parse(d).year for d in df.date]
df['month'] = [parse(d).strftime('%b') for d in df.date]
years = df['year'].unique()
# Draw Plot
mycolors = ['tab:red', 'tab:blue', 'tab:green', 'tab:orange', 'tab:brown', 'tab:grey', 'tab:pink', 'tab:olive', 'deeppink', 'steelblue', 'firebrick', 'mediumseagreen']
plt.figure(figsize=(16,10), dpi= 80)
for i, y in enumerate(years):
plt.plot('month', 'traffic', data=df.loc[df.year==y, :], color=mycolors[i], label=y)
plt.text(df.loc[df.year==y, :].shape[0]-.9, df.loc[df.year==y, 'traffic'][-1:].values[0], y, fontsize=12, color=mycolors[i])
# Decoration
plt.ylim(50,750)
plt.xlim(-0.3, 11)
plt.ylabel('$Air Traffic$')
plt.yticks(fontsize=12, alpha=.7)
plt.title("Monthly Seasonal Plot: Air Passengers Traffic (1949 - 1969)", fontsize=22)
plt.grid(axis='y', alpha=.3)
# Remove borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(0.0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(0.5)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(0.0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(0.5)
# plt.legend(loc='upper right', ncol=2, fontsize=12)
plt.show()
Groups
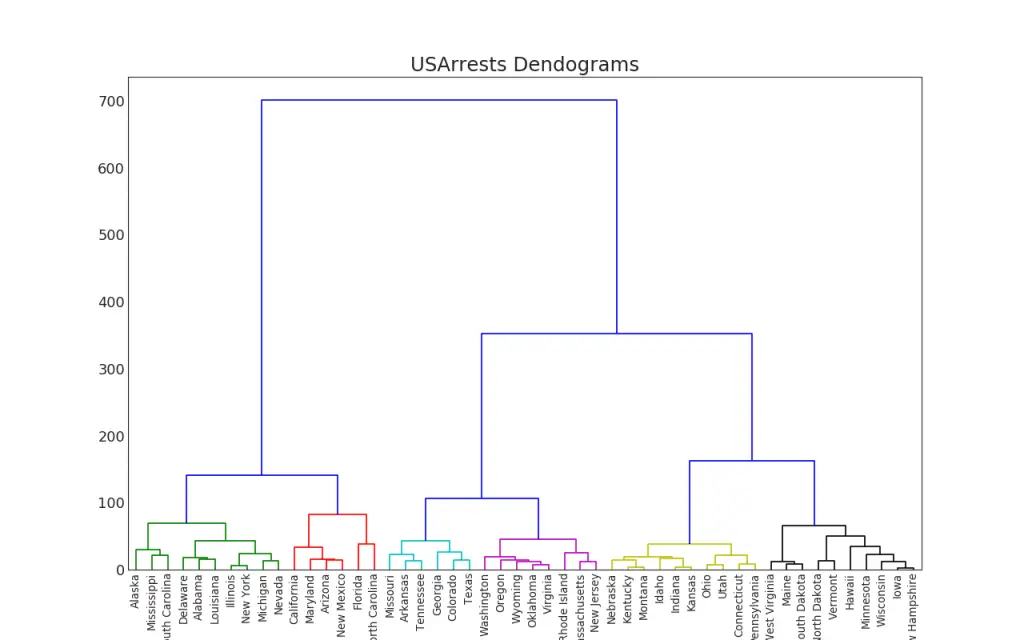
47. Dendrogram
A Dendrogram groups similar points together based on a given distance metric and organizes them in tree like links based on the point’s similarity.
import scipy.cluster.hierarchy as shc
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/USArrests.csv')
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10), dpi= 80)
plt.title("USArrests Dendograms", fontsize=22)
dend = shc.dendrogram(shc.linkage(df[['Murder', 'Assault', 'UrbanPop', 'Rape']], method='ward'), labels=df.State.values, color_threshold=100)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
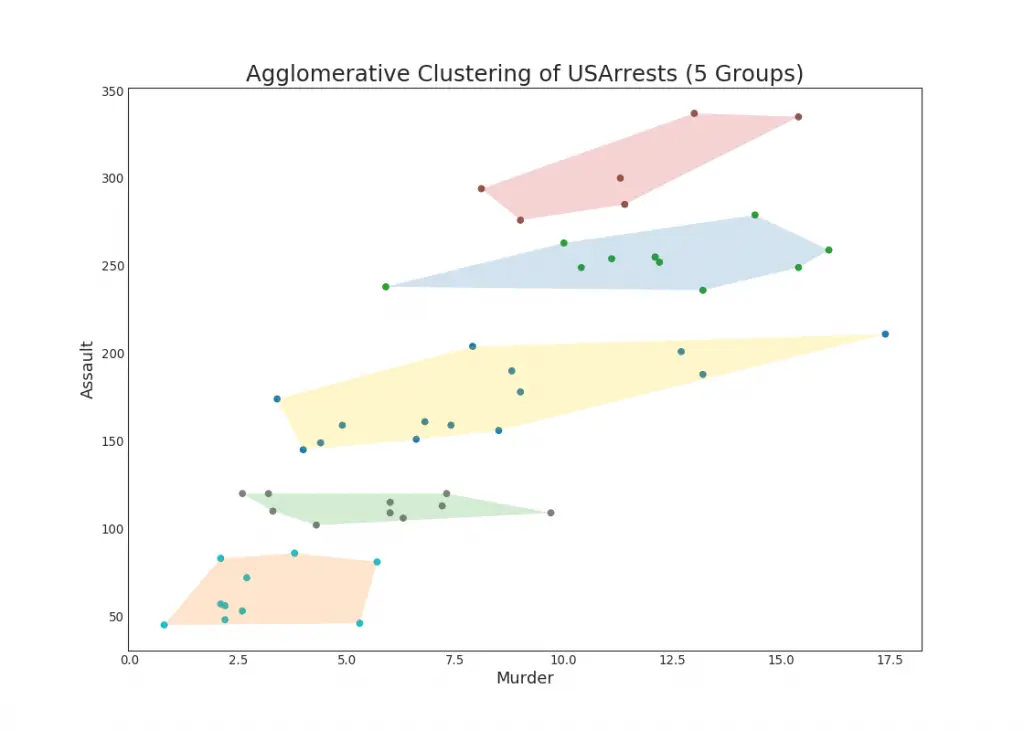
48. Cluster Plot
Cluster Plot canbe used to demarcate points that belong to the same cluster. Below is a representational example to group the US states into 5 groups based on the USArrests dataset. This cluster plot uses the ‘murder’ and ‘assault’ columns as X and Y axis. Alternately you can use the first to principal components as rthe X and Y axis.
Show Codefrom sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClustering
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
# Import Data
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/USArrests.csv')
# Agglomerative Clustering
cluster = AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=5, affinity='euclidean', linkage='ward')
cluster.fit_predict(df[['Murder', 'Assault', 'UrbanPop', 'Rape']])
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10), dpi= 80)
plt.scatter(df.iloc[:,0], df.iloc[:,1], c=cluster.labels_, cmap='tab10')
# Encircle
def encircle(x,y, ax=None, **kw):
if not ax: ax=plt.gca()
p = np.c_[x,y]
hull = ConvexHull(p)
poly = plt.Polygon(p[hull.vertices,:], **kw)
ax.add_patch(poly)
# Draw polygon surrounding vertices
encircle(df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 0, 'Murder'], df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 0, 'Assault'], ec="k", fc="gold", alpha=0.2, linewidth=0)
encircle(df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 1, 'Murder'], df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 1, 'Assault'], ec="k", fc="tab:blue", alpha=0.2, linewidth=0)
encircle(df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 2, 'Murder'], df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 2, 'Assault'], ec="k", fc="tab:red", alpha=0.2, linewidth=0)
encircle(df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 3, 'Murder'], df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 3, 'Assault'], ec="k", fc="tab:green", alpha=0.2, linewidth=0)
encircle(df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 4, 'Murder'], df.loc[cluster.labels_ == 4, 'Assault'], ec="k", fc="tab:orange", alpha=0.2, linewidth=0)
# Decorations
plt.xlabel('Murder'); plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('Assault'); plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.title('Agglomerative Clustering of USArrests (5 Groups)', fontsize=22)
plt.show()
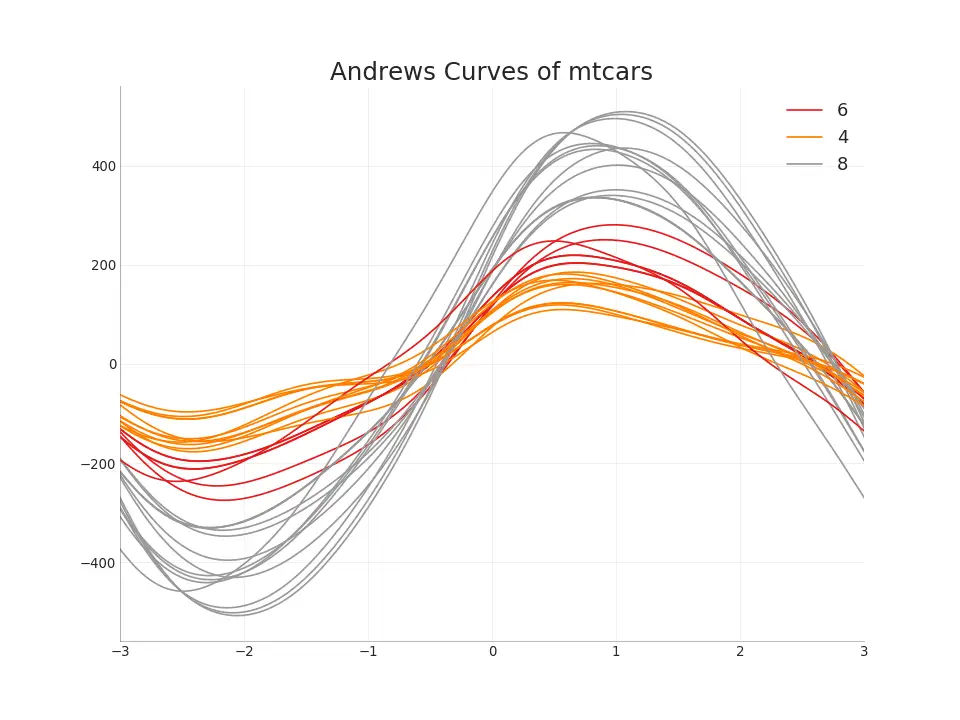
49. Andrews Curve
Andrews Curve helps visualize if there are inherent groupings of the numerical features based on a given grouping. If the features (columns in the dataset) doesn’t help discriminate the group (cyl), then the lines will not be well segregated as you see below.
from pandas.plotting import andrews_curves
# Import
df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/selva86/datasets/raw/master/mtcars.csv")
df.drop(['cars', 'carname'], axis=1, inplace=True)
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(12,9), dpi= 80)
andrews_curves(df, 'cyl', colormap='Set1')
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.title('Andrews Curves of mtcars', fontsize=22)
plt.xlim(-3,3)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
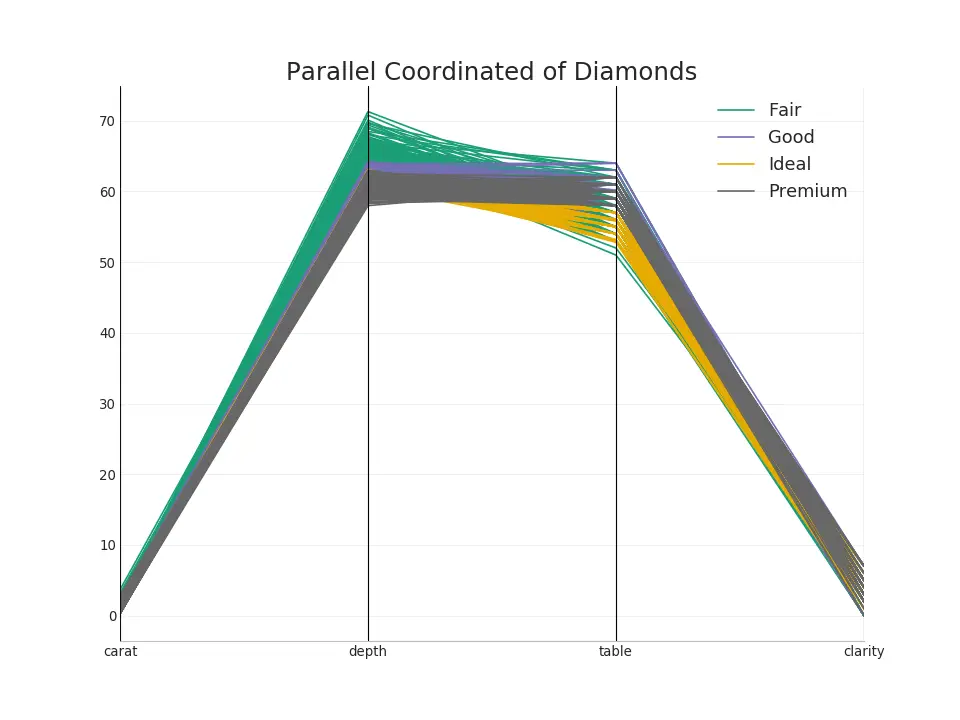
50. Parallel Coordinates
Parallel coordinates helps to visualize if a feature helps to segregate the groups effectively. If a segregation is effected, that feature is likely going to be very useful in predicting that group.
from pandas.plotting import parallel_coordinates
# Import Data
df_final = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/selva86/datasets/master/diamonds_filter.csv")
# Plot
plt.figure(figsize=(12,9), dpi= 80)
parallel_coordinates(df_final, 'cut', colormap='Dark2')
# Lighten borders
plt.gca().spines["top"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["bottom"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.gca().spines["right"].set_alpha(0)
plt.gca().spines["left"].set_alpha(.3)
plt.title('Parallel Coordinated of Diamonds', fontsize=22)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.show()
That’s all for now! If you encounter some error or bug please notify here.